Biologics have revolutionized the pharmaceutical industry and positively influenced the way chronic and severe diseases are being treated. However, with patent expiry of the majority of these biologics, the pharmaceutical industry has had to invent new ways of producing drug products that act the same way as these agents - thus, biosimilars.
What is a biosimilar?
As the name implies, biosimilars are similar versions or copies of biologics approved by regulatory agencies (such as the US Food and Drug Administration, Canadian Health, EMA, etc.) to treat the same diseases and conditions as the original biologic drug. They are not entirely new drugs but rather a structural replica of the original drug. Before they can be marketed, biosimilars, like every other drug, have to go through strict clinical evaluation processes, testing, and trials to ensure pharmaceutical efficacy, quality and safety. These drug products are used to treat difficult and long-term conditions such as HIV, cancer, Alzheimer's diseases, diabetes, psoriasis, etc.
Unlike small molecule drugs, biosimilars are not considered to be generic drugs as they are not exact copies of the reference biologic medicine and do not perform the same functions. Almost every small molecule drug has a generic drug as its counterpart.
A biosimilar is a biological molecule or medicine that is similar in structure, efficacy, safety, immunogenicity profile, and function to a previously existing and approved reference biologic drug. Like biopharmaceutical drugs, biosimilars are also manufactured from living sources and are tested and approved based on the same standards as biologic medicines. Given the inherent variability in the manufacturing process, the regulatory process may be a challenging task to regulatory agencies.
Nevertheless, the biosimilar will be approved if the extent of variability does not affect the efficacy, safety and quality of the biosimilar. That is, a biosimilar will be licensed if no clinically meaningful difference found between it and the original biologic. As opposed to biologic medication products, biosimilars are cost-effective and more accessible to patients, making them the go-to alternative for patients, pharmacists, physicians, and sponsors.
What comprises a biosimilar?
Biosimilars comprise of similar recombinant proteins (peptides or polypeptides comprised of amino acids), sugars, or nucleic acids (RNA or DNA) as the innovator or reference product. The structural composition of each biosimilar is dependent on its complexity, size, genetic modification, cell-line, the desired end-product and its purpose. For example, the biosimilar products of adalimumab (a monoclonal antibody that contains amino acids, sulfide bonds, and glycosylation) also have similar structures that are derived from a different cell-line. A popular example of the approved biosimilar for adalimumab is Amjevita (adalimumab-atto). This also applies to every other biosimilar, and their FDA approved biological drugs.
What is a biosimilar used for?
A biosimilar (interchangeable biosimilar), like every other biologic drug product and other drugs, is used to produce therapeutic effects and clinical results. Biosimilars are used for treatment, diagnosis, prevention, and cure of numerous chronic and dilapidating diseases. The medicinal and clinical effects they produce is dependent on the actions of the reference product they are manufactured from. This is because they both have a similar mechanism of action and are wired to produce similar results. For instance, Inflectra (Infliximab-dyyb), an approved biosimilar to Remicade (Infliximab), can be used for the treatment of ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, etc. These drug products are cheap and readily available, thereby increasing patient access to them.
How biosimilars work
The majority of biologics comprise of one or more large and complex molecules and are used for the treatment of severe long-term conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, cancer, diabetes, HIV/AIDS, and many others.
Biosimilars contain similar active properties as biologic products and produce the same therapeutic effects and results too. Thus, they can be used to treat the same illnesses as their already approved reference products. However, because biosimilars aren't identical to their originator medicines because they are too complex to replicate, biosimilar manufacturers must make efforts to produce biosimilars that are highly similar in composition, safety, efficacy and results before market authorization.
What makes biosimilars effective?
Biosimilars are highly effective because they are manufactured from similar biologic sources, scrutinized according to the same standards, administered in the same way, and have the same potency, dosage, and potential side effects as the approved reference product. Biosimilars are manufactured following the current good manufacturing practices (CGMP) requirements. This includes the facilities, techniques, and controls associated with the processing, manufacturing and packaging of the biosimilars.
Biosimilar drug products are useful in the treatment of autoimmune diseases, diabetes, cancer, etc. As a result of the strict and rigorous regulatory processes, these near-identical biologic products can be interchanged with their reference products during treatment without a change in efficacy or effects.
However, some healthcare professionals and patients have raised concerns that biosimilars may not be as effective or safe as the originator biologics. But these concerns are thought to be raised because biosimilars are recent treatment options. It is expected that every FDA approved drug has been adequately evaluated and tested and have shown no clinically meaningful difference from the reference biologic product. These products can be trusted to produce the same clinical effect as their biologic counterparts.
How are biosimilars involved in medical development?
Biosimilars have had a significant favorable influence on medical developments and have impacted the healthcare industry in multiple positive ways. Their effect on cost savings is expected to create extra funds which will, in turn, give room for regulators and sponsors to invest in and fund other new therapeutic innovations for the treatment and alleviation of diseases.
Based on its transformation of the medical approach to patients living with chronic and severe diseases, biosimilars have moved medical development to a new level. This new approach gives patients easy access to alternative biologics for treatment, cure and prevention of health conditions. Medical fields that have greatly benefited most from this are rheumatology, oncology, and gastroenterology.
The provision of biosimilars for expired patents of drugs used for the treatment of chronic diseases in each of these fields is an added advantage. For example, there's been an immediate replacement of drugs such as Remicade (Infliximab) for the treatment of ulcerative colitis, Crohn's diseases, inflammatory bowel disease, etc., and Herceptin (trastuzumab) - for the treatment of gastric and breast cancer and several others with their corresponding biosimilar products.
The economic impact on the healthcare industry also gives room for growth as well as new medical innovations. In addition to this, due to the variety of biosimilars available, there is biosimilar competition in the industry, and this promotes growth.
What are the recent biosimilar developments?
With several biologics facing patent expirations and many others prone to a patent expiration in the nearest future, it is expected that the biosimilar industry will experience some considerable growth changes. Also, with patent expiration, the majority of healthcare professionals have eyes on biosimilars as a cheaper and more accessible biologics option compared to originator biopharmaceuticals.
As of the end of 2019, about 26 biosimilars were approved in the US, as well as four follow-on biologicals, while Europe had 58 approved biosimilars. Some US approved biosimilars include, Retacrit, Abrilada, Basaglar, Lusduna, Admelog, Mvasi (bevacizumab-awwb), Erelzi (etanercept-szzs), Ogivri (trastuzumab-dkst), etc. Some Europe-approved biosimilars include, Omnitrope, Movymia, Mvasi, Idacio, Flixabi, Inflectra, Erelzi, Terrodsa, Trazimera, Truxima, etc.
In 2020, SomaLogic started a new collaboration with the FDA to help advance and boost biosimilar development. This is a five-year agreement that will involve the use of data generated from proprietary proteomic technology at SomaLogic to discover and identify the popular pharmacodynamic biomarkers used for therapeutic biologics. The biomarkers found will then be compared to biomarkers produced by biosimilar drugs.
How are biosimilars produced?
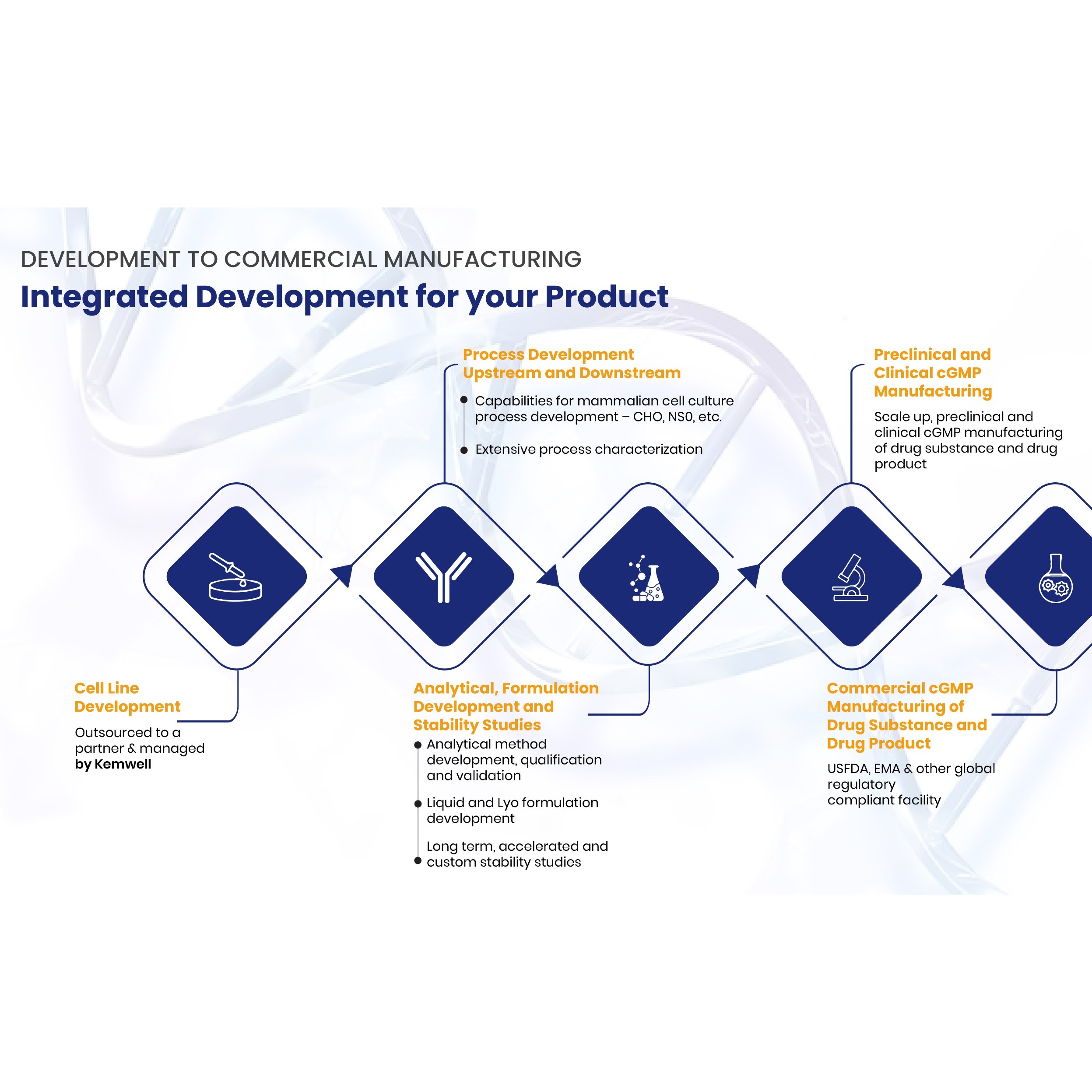
Biosimilar drug products are highly complex and large molecules produced from natural sources through a multiple-step manufacturing process. The essential characteristics of each biosimilar product are its critical quality attributes (CQAs). These attributes vary between biosimilars depending on the manufacturing process or the post-translational modifications that occur within the cellular environment. The CQAs of these molecular products must be matched with the reference biologics to ensure high-similarity. Biosimilars are developed, tested, and approved based on the "totality of evidence" criteria. This criterion confirms the replication or high-similarity between biosimilars and reference biologics through multiple functional and structural comparisons.
Before biosimilars are approved for marketing, they undergo several processes to ensure efficacy and safety. The first step, after the manufacturing process, is analytical evaluation and comparisons to ensure that the biosimilar manufactured closely matches the originator product in function and structure. Afterwards, a preclinical and clinical trial is carried out, extrapolation, and substitution and interchangeability tests and finally, approval for public marketing and consumption.
How is biosimilarity or interchangeability determined?
Interchangeability refers to the medical practice of substituting or changing a pharmaceutical product for another to achieve the same therapeutic effects and clinical results. One benefit and challenge of biosimilars is interchangeability with their specific reference products. As a result of clinical similarity in efficacy, safety, quality and immunogenicity, this may present as a major challenge. Therefore, before biosimilar approval, their interchangeability with their specific innovator products must be determined to ensure the safety of the patient. Until a regulatory agency such as FDA, EMA or Canadian Health approves a biosimilar as interchangeable, it is not considered suitable for substitution in any clinical setting.
To determine the biosimilar interchangeability of these large molecule products, the FDA has issued a drafted guide for demonstrating interchangeability and specific analytical assessment and additional data that must be observed before a biosimilar can qualify as interchangeable. However, there are currently no FDA approved interchangeable biosimilars yet. Also, to obtain interchangeability, sponsors of the manufacturing companies and process need to carry out thorough and comparative pharmacokinetic studies based on various switches or substitutions and then, an extended follow-up period.
Based on FDA standards, manufacturers of proposed interchangeable biosimilars must be able to prove that the risks - in terms of efficacy levels or safety, when substituted or switched between the biosimilar product and its reference product is not greater than the risk associated with using the reference product without alternation or interchanging. In the United States, state laws govern automatic substitutions at pharmacies. Nevertheless, without pharmacy-level permission for substitutions, the substitution of biosimilars for biologic products can be carried out at hospitals, health plans, etc., using "therapeutic interchange."
Some of the significant risks associated with substituting or switching between biosimilars and biologic products include reduced efficacy and increased immunogenicity. A study was carried out to examine the interchangeability in the treatment of Crohn's disease and Ulcerative colitis in eight patients following a switch to Infliximab biosimilar after 48 weeks of the reference biologic products. Six, out of eight of these patients adapted well to the biosimilar and continued on remission, while the remaining two didn't. Due to the small number of patients (sample size) on which the cohort study was carried out, researchers found it difficult to extrapolate the findings to a larger population.
Which companies make biosimilars?
A few years after the first biosimilar was approved in 2015 and several biosimilar manufacturing companies have sprung up. Some companies indulge solely in manufacturing biosimilars while a few others diversify. Drugmakers are consistently investing in the biosimilar space, leading to the rapid development of the biosimilar industry.
With the increasing need for biosimilars, it is only expected that more biosimilar manufacturing companies will spring up in a few years from now. However, some established biosimilar manufacturing companies include Hospira, Sandoz, Pfizer, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Bioton, Biocad, Biosidus, Biogen, Amega Biotech, Biocon, Zydus Cadila, Dr Reddy's Laboratories, Ranbaxy, 3SBio, Qilu Pharmaceutical, Mylan, Sandoz, Probiomed, Celltron, LG Life Sciences, etc.
What are the benefits of using biosimilars?
Biosimilar adoption and manufacturing in the pharmaceutical industry has provided biologic drug users (patients), healthcare professionals and the healthcare industry with several benefits. The major benefits of biosimilars to health consumers is drastically reduced cost. With biosimilars, patients can have access to cost-efficient healthcare without a compromising treatment quality and standard. Also, the healthcare industry benefits largely as a result of reduced healthcare savings.
Who will benefit from biosimilar cost savings?
Biosimilars are regarded as cost-effective versions of expensive biologic products. A biosimilar medicine will, on an average cost 15 to 20 percent less compared to brand-named reference products. This is as a result of the rigorous manufacturing and regulatory process that the originator products undergo. A recent study revealed that direct spending on reference biologic drugs might reduce by USD 54 billion from 2017-2026. This comprises about 3% of the previously estimated value of biologic products over this period, with a range of $24 billion to about $150 billion.
With the use of biosimilars, patients can save up to 17 percent of their out-pocket costs on an average. Also, the Medicare market can benefit from the cost savings, as well as the commercial market, each saving up to $1.2 billion and $3.3 billion averagely on an annual basis. In addition to this, biosimilar medicines, based on coinsurance, can reduce cost-sharing by cutting out-of-pocket spending of patients.
Which biologic treatments have biosimilars made available?
Biosimilars have made several biologic treatments available to patients and the healthcare system. Through biosimilars, treatment options for diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's diseases, cancer, ankylosing spondylitis, etc., have been made readily available and at a lower price without compromising the treatment standard.
As of June 2019, there were a total of twenty biologics with FDA-licensed biosimilars. Some include Trastuzumab (Herceptin) - Trastuzumab-dkst (ogivri), Trastuzumab-pkrb (Herzuma), Filgrastim (Neugopen) - Filgastrim-aafi (Nivestym), Filgastrim-sndz (Fulphila), Rituximab, Etanercept, Epoetin Alpha, Adalimumab, PegFilgastrin, Bevacizumab, etc. The biosimilar product launch of each of these products fell within the first half of 2019.
These biosimilars were created to treat various health conditions such as autoimmune diseases, cancer, rheumatoid diseases, etc. A popular example is Truxima (a biosimilar to rituximab) used for the treatment of cancer, non-Hodgkins Lymphoma particularly. Also, Ogivri (a biosimilar to trastuzumab), is used for the treatment of specific breast and gastric cancers. Some biosimilars are used to treat or cure multiple health conditions. For example, the biosimilar to the reference biologic, adalimumab can be used to treat various types of arthritis including ankylosing spondylitis, inflammatory arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, etc., and other conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease.
Also, certain health conditions can be treated with more than one approved biosimilar medicine. For example, rheumatoid arthritis can be treated by several biosimilars. In very few cases, off-label biosimilars can be prescribed by physicians should an important need arise.
References
https://www.giiresearch.com/report/kt288682-pharma-leader-series-top-25-biosimilar-drug.html
https://www.thebalance.com/what-is-a-biosimilar-drug-4042688
http://www.gabionline.net/Biosimilars/News
https://www.biosimilardevelopment.com/solution/biosimilar-manufacturing
https://www.google.com/amp/s/pharmanewsintel.com/news/amp/top-challenges-facing-biosimilar-adoption-manufacturing
https://www.amgenbiosimilars.com/bioengage/regulatory-approval-pathways/Determining-Interchangeability
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6107532/#!po=3.33333
References


































































.jpg)
.jpg)























































.png)


.png)



.jpg)