Neofact® - Medical device for surfactant application
Product Description
Lyomark Pharma GmbH

-
DE
-
2015On CPHI since
Company types
Categories
Specifications
Lyomark Pharma GmbH

-
DE
-
2015On CPHI since
Company types
More Products from Lyomark Pharma GmbH (2)
-
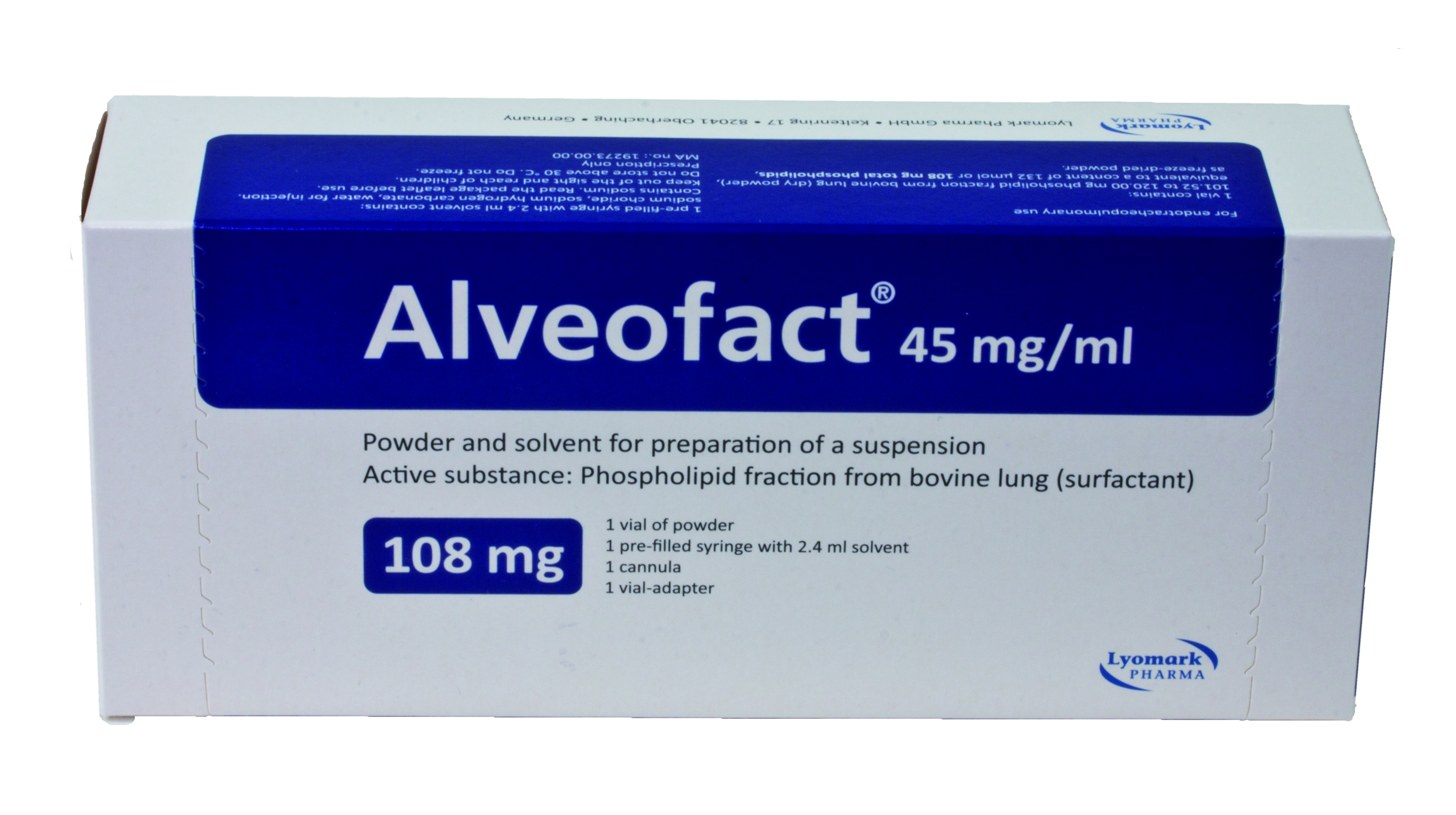
Product Alveofact® - Natural bovine lung surfactant
Alveofact is used in neonates. Preventive use in premature neonates with a high risk of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS).
Active substance: Phospholipid fractionfrom bovine lung (surfactant) -
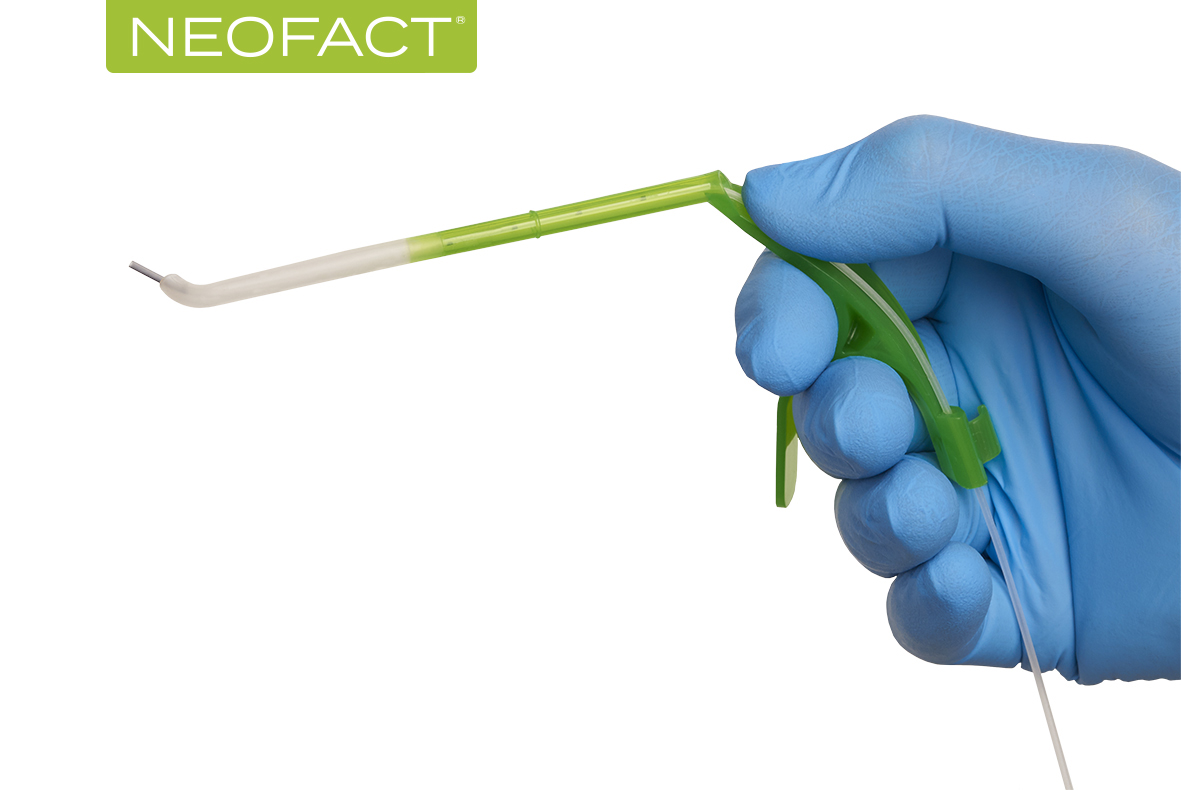
Product Neofact - Clinical evaluation of an application aid for less-invasive surfactant administration (LISA)
Neofact, by Lyomark Pharma, is a medical device for neonates suffering from RDS.
This study shows that the LISA method (less invasive surfactant administration) via Neofact® appears feasible.
Neofact® makes surfactant application easy and is also suitable for all gesta...
Lyomark Pharma GmbH resources (2)
-
News Neofact - Clinical evaluation of an applicator for surfactant administration
Neofact, by Lyomark Pharma, is a medical device for neonates suffering from RDS.
This study shows that the LISA method (less invasive administration) via Neofact® appears feasible.
Neofact® makes surfactant application easy and can also be used at any gestational age.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33023914/ -
Technical Data Neofact® - Feasibility study
In the clinical study carried out at the University Hospital Tübingen, 20 premature infants (gestational age ≥26 + 0/7) were administered surfactant Alveofact® (45 mg / mL; Lyomark Pharma, Oberhaching, Germany) using the new LISA application aid Neofact®. The aim of developing Neofact® was to enable a simple and gentle process for surfactant application that works without the use of Magill forceps. Neofact® makes surfactant application easy and is also suitable for all gestational ages. This was confirmed in the study and the results of the study are convincing. An extremely high success rate could be achieved (95%), complications seemed rear.
Further information on the study can be found: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33023914/
Position your company at the heart of the global Pharma industry with a CPHI Online membership
-
Your products and solutions visible to thousands of visitors within the largest Pharma marketplace
-
Generate high-quality, engaged leads for your business, all year round
-
Promote your business as the industry’s thought-leader by hosting your reports, brochures and videos within your profile
-
Your company’s profile boosted at all participating CPHI events
-
An easy-to-use platform with a detailed dashboard showing your leads and performance