- Home
- Finished Dosage Forms (Products)
- Out-licensing
CPHI Online is the largest global marketplace in the pharma ingredients industry
-
Products551,744
-
Companies7,781
-
Articles11,636
-
Events8
-
Webinars342
Out-licensing
Out-licensing Companies (81)
Out-licensing News
-
News 85 years pharmaceutical manufacturing
Adelco will be celebrating this year 85 years of Manufacturing, Established in 1934, Adelco has acquired a wealth of experience and respect locally and internationally.12 Jun 2019
Out-licensing Products (328)
-
Product Cogiton
Cogiton is a patented food supplement based on a specific and harmonized combination of Ginkgo Biloba, B vitamins, carnosine, coenzyme Q10, L-cysteine, beta-carotene, vitamin E, vitamin C and selenium.
Cogiton is a drinkable food supplement available in PET vials with a dosing cap, easy to us...
-
Product Food supplements
A complete line of ready-to-market food supplements for licensing covering the following areas: respiratory tract, urinary tract, hair loss, energy, memory, immune system, proctology, skin aging, sleep disorders and jet lag.
-
Product CORTEXIUM - food supplement for improving brain function and concentration
CORTEXIUM is designed to enhance brain function, improve concentration, and reduce fatigue by providing a blend of scientifically proven ingredients.
It fills this gap by offering a synergistic blend of ingredients such as GABA, essential vitamins, minerals, and PQQ to enhance brain ...
-
Product Lisdexamfetamine
Lisdexamfetamine is used to treat ADHD in children and adults. Lisdexamfetamine capsules come in six strengths, 20mg, 30mg, 40mg, 50mg, 60mg and 70mg. Pivotal BE study is completed and passing. Coripharma will finalize the dossier in Q4 2024 and start submitting for our clients in January 2025.
-
Product Product nursing (distribution & promotion)
"Product Nursing" is the Jakin group solution to full-outsource your pharmaceutical, parapharmaceutical and medical device products in Italy. Product Nursing combines the normal distribution and product logistics activity with the excellence and leadership of Jakin group in multi-channel medical-scien...
-
Product FEMAGINAL PLUS ovules
FEMAGINAL PLUS ovules is a medical device Class IIa based on an improved formula of Boricacid, Hyaluronic acid, Polycarbophyl, Lactic acid, Tocopheryl acetate, Vitamin A, 18-Betaglycyrrhetinicacid and Tea tree oil, indicated in the treatment of vaginal dryness, irritations, burning and infections.
Wom...
-
Product Tadalafil soft caps
GAP specialises in innovative generics. GAP has developed TADALAFIL in soft caps offering unique marketing opportunities compared to standard generics in tablets.
Indications:Genito-urinary System Erectile dysfunction
Only 5 mg: benign prostatic dysfunction
Only 20 mg: treat pulmon...
-
Product FEXUCLUE®
Fexuclue (Fexuprazan) is the best-in-class novel anti acid secretion agent with rapid onset time and potent acid suppressive effect, addressing the growing unmet needs of PPIs
Highlights of Fexuclue are: * Launched in Korea (2022) and Philippines (2023)
* Approved in Chile and Ecuador qq...
-
Product medEctoin Allergy Eye Drops
Medical device for treatment and prevention of allergic conjunctivis symtoms.
• Quick symptoms reduction like itching, tearing and irritation within 30 seconds • Alleviates allergic symptoms (red, itchy and watery eyes) • Reduces allergen induced inflammations of the conjunctiv...
-
Product ROSUMEGA®
(1) Mixed Hyperlipidemia
(2) Once daily, 2~4 soft capsules per day
(3) Dual Effect to reduce LCL-C and TG Level by patented technology* (3-layer coating)
(4) Combo’s additional decrease effect in residual cardiovascular risk & Omega-3’s multiple effects
(Lower...
-
Product Ibuprofen + Pseudoephedrine 400/60mg, 200/30 mg
Type: OTC Medicinal Product
Pharmaceutical form: Tablets
Package: 10, 20 tablets
Active pronciple:
1 tablet contains 200/400 mg ibuprofen (Ibup...
-
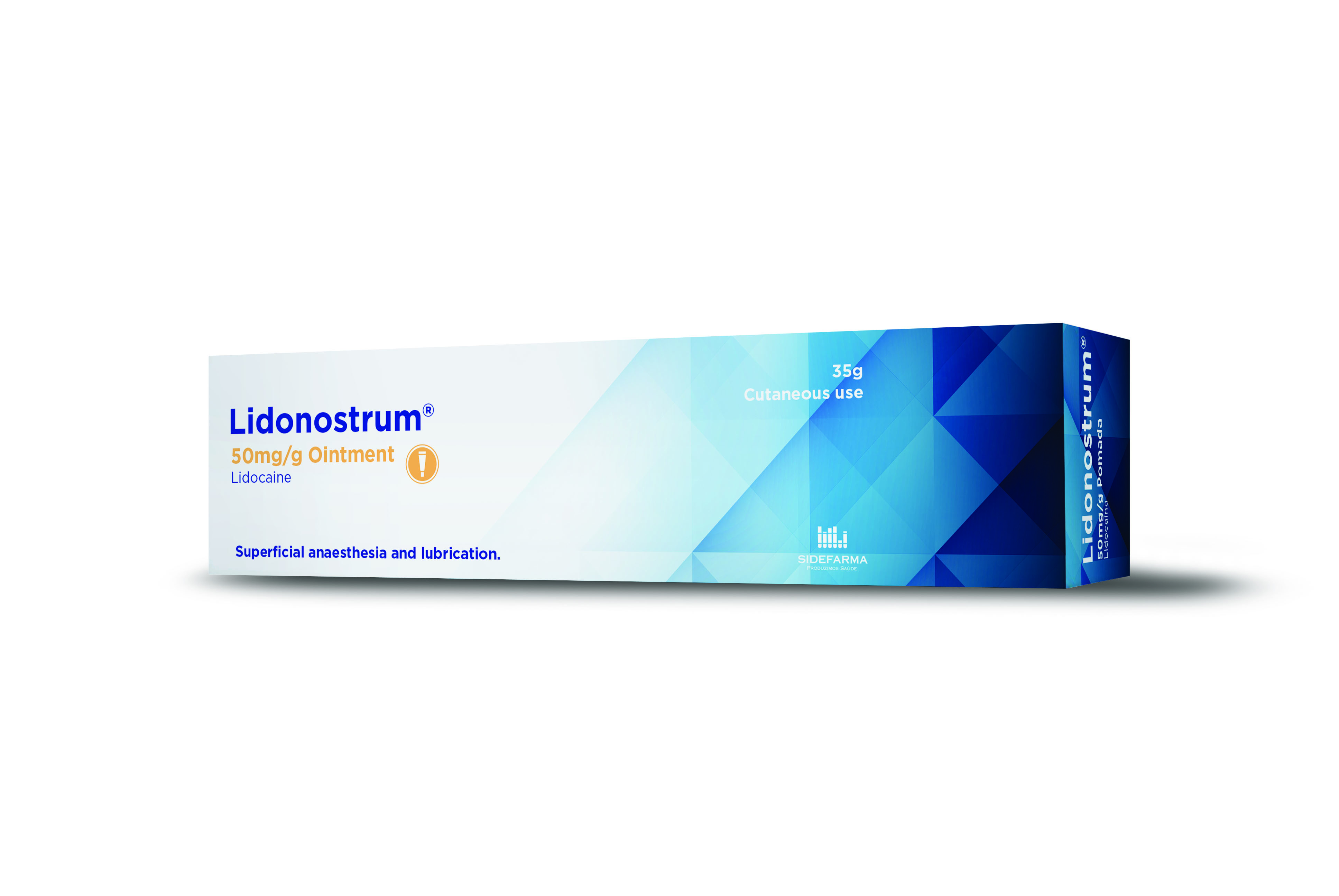
Product Lidonostrum (Lidocaine ointment, 50 mg/g)
Dosage strength: 50 mg/g. Pharmaceutical form: ointment. Therapeutic indications:
- Temporary relief of the pain caused by burns and mild skin abrasion, such as sunburns, Herpes zoster and cold sores (herpes simplex labialis), sore nipples and insect bites.
- Anaesthes...
-
Product Libicare Meno
Integral management of all menopause signs and symptoms 24 hours a day:
· Food supplement. Patented Formulation.
· Target Patients: Women that suffer from menopause symptoms and wish to feel good and live their life to the fullest....
-
Product AQaffron
The only natural adjuvant therapy to antidepressant with proven therapeutic results comparable to pharmaceutical solutions. No side effects. AQaffron is an extremely effective antidepressant aid, demonstrated by our multiple clinical studies on the finished formulation.
-
Product Doxylamine DTM
• Active Ingredient(s): Doxylamine Succinate 12.5/15/25 mg • Unit size: 7/10/14 tablets o sticks per box • Product Description: Useful in the symptomatic treatment of all types of insomnia. Its efficiency is proven from the first night dose. Direct to mouth, no water needed, easy administration, easy to...
-
Product Paracetamol 500 mg - EFFERVESCENT TABLETS/SOLUBLE GRANULES/ODG in stick
Cold&Flu/Painkillereffervescent tablets in tube
soluble granules in stick
ODG in stick
Available for outlicensing worldwide.
Contact us for more info
-
Product USFDA Oral Solid Dosages
USFDA Oral Solid Dosages in major Therapeutic categories. All products are USFDA registered and available in either Zone II or Zone IV stability studies. Full dossiers available in either ECTD or CTD formats
-
Product Amikacin Inj.Sol 500mg/2ml (EU CTD Available) & 1g/4ml (EU CTD Available: Q3 2021)
Amikacin Solution for Injection
Reference Product: Briklin® / BRISTOL-MYERS SQUIBB
Description: Amikacin sulfate is indicated in the short-term treatment of serious infections due to susceptible strains of Gram-negative bacteria, including Pseudomonas species,&nb...
-
Product Breathy nasal
Indications
Relief of nasal congestion due to colds, allergic, low humidity, nose bleeding and other irritation.
Each ml of BREATHY nasal drops contains:
Sodium chloride………….. 6.5 mg
Package : Box of 1 nasal drop bottle @ 30 ml

-
Product Famotidine 20 mg
Biofarm Sp. z o.o. offers a wide range of pharmaceutical products which includes Famotidine Biofarm.
Category: OTC
Therapeutic class: Gastroenterology
Api + strength: Famotidine 20 mg.
Form: tablets.
Main Indication: indigestion, heartburn and acidity
Contact us for more inform...
-
Product Broncositol® oral supplement
The only myo-inositol-based dietary supplement specifically designed to manage respiratory diseases
Supports the maintenance of the physiological state of the respiratory system by promoting the health of mucous membranes and the production of lung surfactants
The inclu...
-
Product ALCOFILTRUM ®
Hangover symptoms relief
• Blend of natural ingredients: Lignin Hydrolyzed (Enterosorbent) + selected Vitamins • Binds to toxins within the GI tract, such as Fusel Alcohols • Reduces the negative effect of alcohol consumption • Clinically tested solution OEM option available

-
Product Eribulin Mesylate Injection
Generic Name: Eribulin Mesylate Injection
Indication: Metastatic breast cancer (CN, US, EU, Japan and other countries)
Liposarcoma (US, EU)
Soft tissue sarcoma (Japan and other countries)
Guidelines:
NCCN (2023V4), CSCO (2023), ESMO (2023)
Exc...
-
Product Out Licensing Dossiers
• Out Licensing • Technology Transfer • Co-Development / Profit Sharing with Technology Partners
API partners
Marketing Partners
&...
-
Product Melatonin Products
Mouth & Throat Spray with Melatonin
Lozenges with Melatonin
100% free from preservatives
-
Product Carbocisteine oral solution 250mg/5ml & 750mg/5ml
Therapeutic category: Mucolytic agent
250mg/5ml is packed in BTx300ml and is registered as generic.
750mg/5ml is packed in BTx100ml, BTx200ml and is registered as hybrid. Added value: 1 spoon daily (vs 3 spoons with lowest strength) and sugar-free.

-
Product Amoxicillin + Clavulanic acid
Centrient Pharmaceuticals provides wide range of drug products which includes amoxicillin + clavulanic acid. Dosage form: film-coated tablets; oral suspension; sachets; injectables. Contact us for more information.
-
Product Irda 150 Mg 28 Film Tablet
Nobel Ilac Sanayii Ve Ticaret A.S provides wide range of pharmaceutical products which includes irda 150 mg 28 film tablet. Active ingredients: irbesartan. Indication: antihypertensive. Contact us for more information.
-
Product Market Access, Launch and Marketing
MEDIPHA SANTE offers a wide range of services which include:- providing all the activities of an “Exploitant” company on the French market for French companies or foreign companies that do not have a pharmaceutical establishment in France
- assistance in the creation of a French subsidiary of your...
-
Product Atorvastatin
Galenicum provides wide range of generics which includes atorvastatin. It's for cardiovascular system. Contact us for more information.
-
Product Dermatology
Hair loss, Anti-seborrheic, Hair care, Cicatrization, Mother and baby care, Bath and hydration, Dry, atopic and psoriatic skin, Anti aging
-
Product Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate 300 mg
- Presentation: Package containing 60 plastic bottles with 30 coated tablets.
- Indication (Brazil Prescription Medicines): First line medication indicated, in combination with other antiretroviral agents, for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults and chronic Hepatitis B.
...
-
Product Betrimine (Vitamins B1, B6 & B12 Solution for injection 250 mg +250 mg +2 mg/5ml)
Therapeutic indications
Neurological diseases caused by severe vitamin B1, B6 and B12 deficiencies that cannot be remedied by means of oral therapy.
Such deficiencies can also lead to peripheral neuropathy, muscle wasting or weakness.
Such deficiencies can also ...
-
Product EU eCTD Dossiers with Finished Product Supply
1. Out-licensing of our eCTD Dossiers covering various stability zones (including IVb), including supply of finished products (from manufacturing sites in Europe with various cGMP certifications from High Regulated Authorities worldwide)
2. Early and first to launch opportunities (generics)
3....
-
Product DEXAMETHASONE soluble tablets
Strength: 0.5 mg/tab; 2 mg/tab; 4 mg/tab; 8 mg/tab; 10 mg/tab; 20 mg/tab Therapeutic area: Glucocorticoid Therapy Innovator: - (-)
-
Product Colostrum Junior
Colostrum Junior is a patented food supplement based on a harmonized combination of bovine colostrum, vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin D3 and vitamin E.
Colostrum Junior is available in chewable tablets; it is recommended to take one tablet per day.
Colostrum clinical effic...
-
Product Templar
Templar is a patented food supplement based on a specific and harmonized combination of Vit. B6, beta carotene, selenium, alpha-lipoic acid, coenzyme Q10 and catechins from green tea (Camellia Sinensis).
Templar is available in vials with a dosing cap, easy to use; it is recommended to take on...
-
Product Afragil
Many women spend almost one third of their lives in menopause. An increase in oxidative stress (OS) levels is observed during the menopause. During this period of time there are many symptoms which have an impact on the women’s quality of life. Currently, there is gap in the treatment of climacteric an...
-
Product Colostrum
Colostrum is a food supplement for the Immune Defense health.
Colostrum is a patented food supplement based on clinically tested bovine colostrum, .
Colostrum is available in chewable tablets; it is recommended to take one tablet per day.
Colostrum clinical efficacy i...
-
Product Eliglustat
Is used to treat Gaucher disease which is a fat storage disorder. Eliglustat is available in 84mg hard capsules. Coripharma`s generic version of Eliglustat is being developed in our R&D facility located in Iceland, which is run solely on sustainable energy. We plan to have the dossier available in Q1 2...
-
Product Macitentan
Macitentan is a medicine that is used to treat Pulmonary arterial hypertension. Macitentan Film-coated tablets has one strength, 10mg, has passed its pivotal bioequivalence study and dossier is available.
Our business development team remains available to discuss opportunities with our customers.
...
-
Product MOMAID – Postpartum Recovery Supplement
Problem Pregnancy and birth places increased stress on the pelvic floor leaving the muscles fatigued and weak. The risk of pelvic floor injury increases with each pregnancy, and it is also associated with age at first vaginal delivery. Regeneration of pelvic floor muscles is important to prevent pelvic flo...
-
Product INCOXIL - Stronger pelvic floor muscles and less urinary incontinence
Unmet need
25 to 57 % of all women in the U.S. experience urinary incontinence (UI). In the USA UI is a significant economic burden.
Solution
Pelvic floor muscle training (PFMT) is globally recommended as part of first-line treatment and is proven to work for ...
-
Product Isotretinoin soft caps
GAP is offering for out licence ISOTRETINOIN soft caps 5-10-20-40mg with the most updated BE study (2018)
GAP manufacturers per year over 250 milion caps of Isotretinoin Product is offered for licensing or contract manufacture agreement
-
Product Calcium & Vitamin D3 Chewable tablet
Strengths:
500 mg / 400 IU
1000 mg / 800 IU
Indication:
Prevention and treatment of calcium and vitamin D deficiency & osteoporosis treatment

-
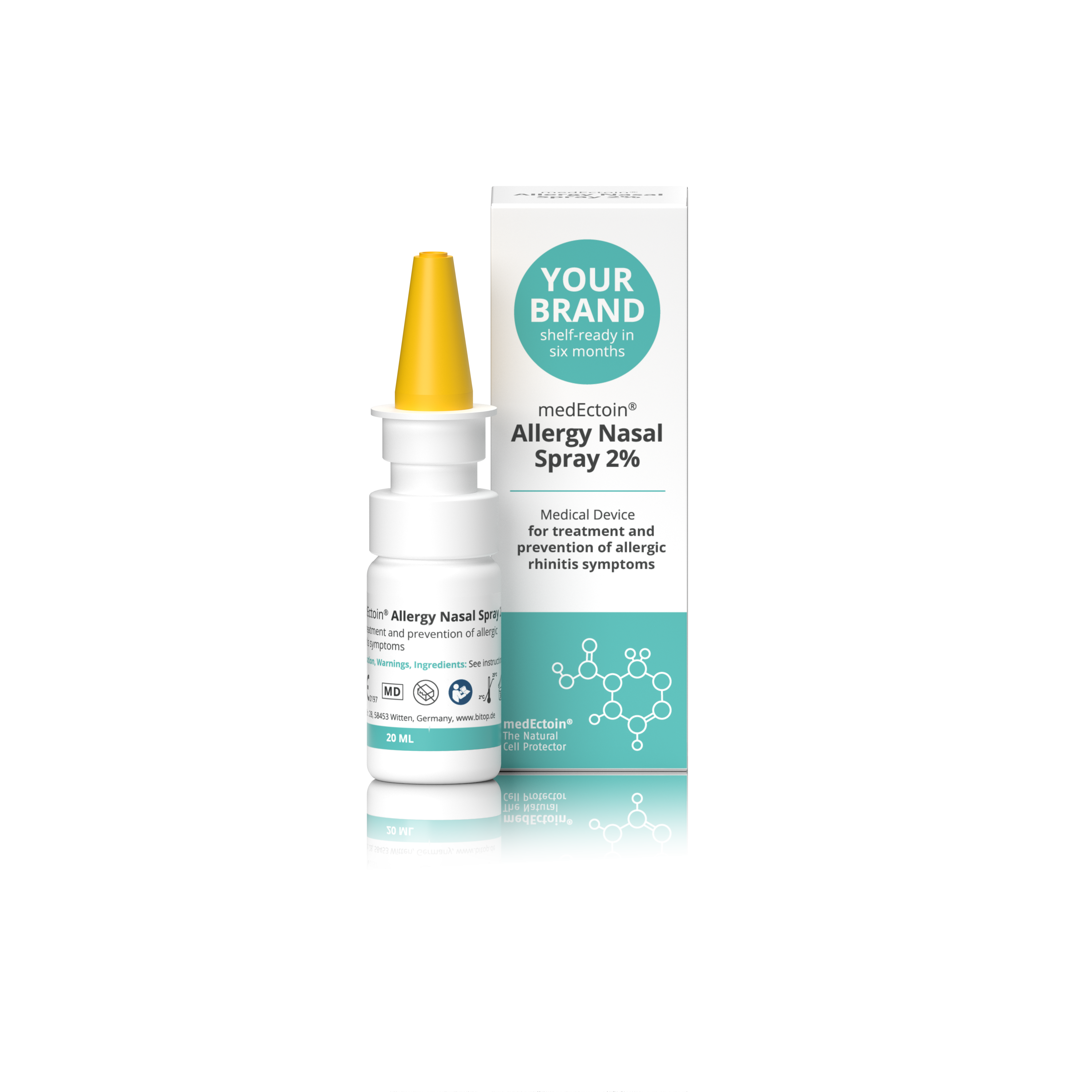
Product medEctoin Allergy Nasal Spray
Medical device for treatment and prevention of allergic rhinitis symtoms. • Alleviates allergic symptoms (itchy and runny nose, sneezing, nasal congestion) • Reduces allergen induced inflammations of the nasal mucosa
• Reduces harmful influences of allergens and airborne particles • ...
-
Product medEctoin Allergy Nasal Spray Forte
Medical device for treatment and prevention of allergic rhinitis symtoms with natural decongestion effect. • Decongests the nose on a natural way • Alleviates allergic symptoms (itchy and runny nose, sneezing, nasal congestion) • Reduces allergen induced inflammations of the nasal mucosa&nb...
-
Product medEctoin Sicca Eye Drops
Medical device for treatment and prevention of dry eyes symtoms.
• Reduces inflammations caused by an irritated or dry conjunctiva • Alleviates symptoms of dry eyes such as burning, dryness, itching etc. • Stabilizes the lipid layer of the tear film
• Moistens dry eyes and...
-
Product medEctoin Sicca Eye Drops + HA
Medical device for treatment and prevention of dry eyes symtoms. • Moistens dry and irritated eyes • Reduces burning and itching • Stabilizes the lipid layer of the tear film and reduces further dehydration • Protects ocular cells from hyperosmolarity • Also effective as preventive t...
-
Product medEctoin Eye Gel
Medical device for treatment and prevention of dry, irritated and inflamed eyes.
• Calms and soothes irritated and tired eyes • Alleviates allergic symptoms (red, itchy and watery eyes) • Intensive and longer moisturization of dry and irritated eyes due to prolonged retention tim...
-
Product medEctoin Inflammation Reducing Eye Drops
Medical device for treatment of inflammatory diseases and the corneal occular surface. • Quick symptoms reduction like itching, tearing and irritation within 30 seconds. • Alleviates symptoms such as burning, dryness, itching, redness, foreign body sensation, etc. • Reduces inflammation...
-
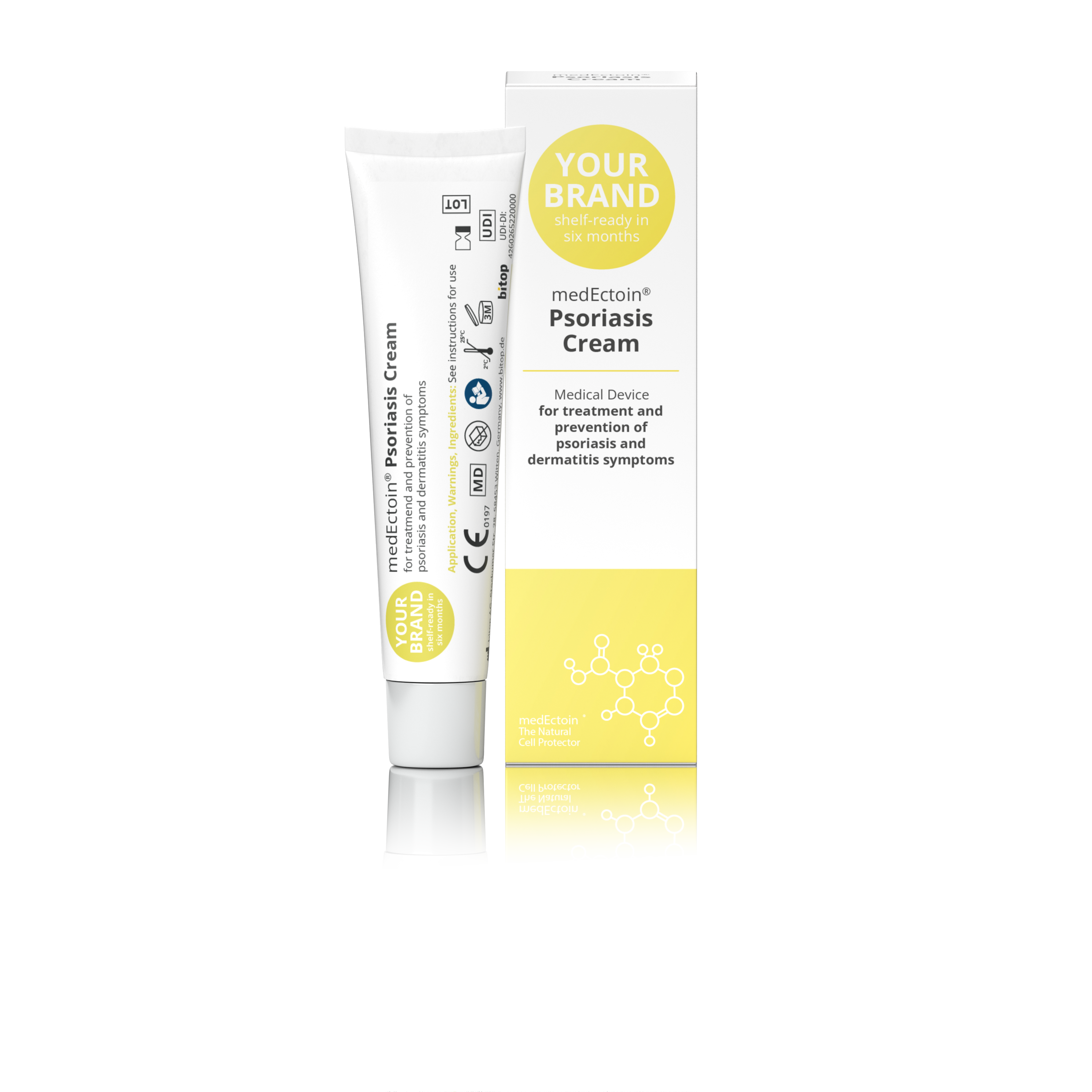
Product medEctoin Psoriasis Cream
Medical device for treatment and prevention of psoriasis and dermatitis symtoms. • Reduces scaling, itching, redness, roughness and hardening of the skin • Supports the natural elimination of dead cells from the skin surface which is a symptom of psoriasis • Relieves and calms irritated and damaged ...
-
Product medEctoin Vaginal Gel
Medical device for the relief of vagina dryness/ vaginal atrophy. • Helps reduce inflammation of the vaginal mucosa • Immediately (10-15 minutes) hydrates dry and irritated vaginal mucosa and prevents further dehydration • Immediately relieves vaginal atrophy symptoms (within 5 days) such as i...
-
Product medEctoin Inhalation Solution
Medical device for supportive treatment to reduce inflammations of the airways. • Supportive treatment and symptom alleviation of diseases of the airways, such as allergic or non-allergic asthma, bronchitis or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) • Protects and moisturizes the mucosa of t...
-
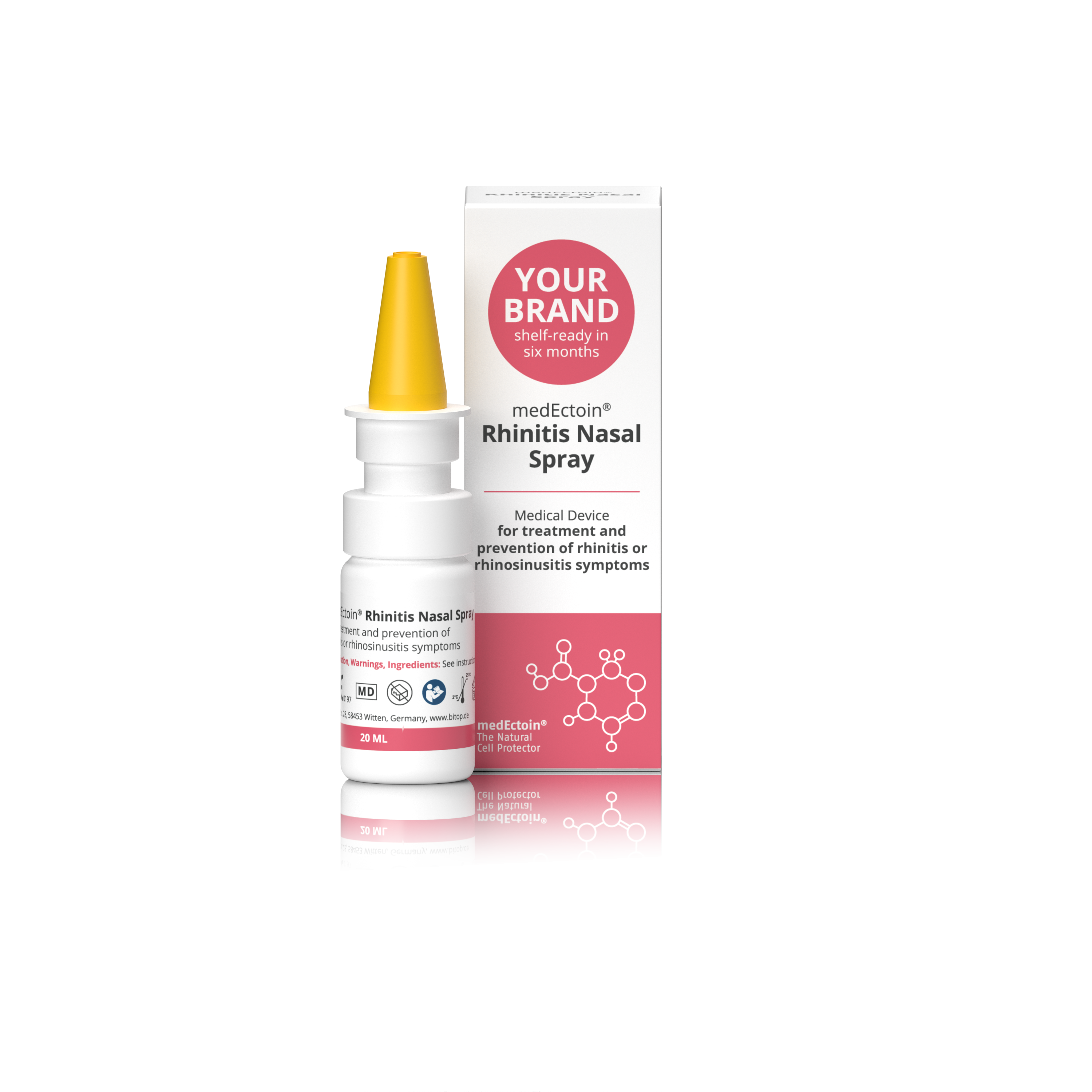
Product medEctoin Rhinitis Nasal Spray
Medical device for treatment and prevention of rhinitis or rhinosinusitis symtoms.
• 4-in-1 effect: Significantly reduces blocked nose, runny nose, facial pain, headache and loss in smell and taste • Reduces inflammations of disturbed nasal mucosa and sinuses caused by rhinitis a...
-
Product JUVIAGEL – Vaginal moisturizing gel
Problem
Vaginal dryness (or atrophy) is a condition caused by a decreased level of the oestrogen hormone. It is characterized by a thinning, dehydrated and possibly inflamed vaginal wall. A dry vagina means uncomfortable or painful sex. In more severe cases it may cause a dry, itchy or even b...
-
Product Leniroid proctologic gel
Treatment for anus rectal disorders causing swelling, inflammation and discomfort. It performs a protective, soothing and antibacterial action in the anus rectal area, reducing and alleviating pain, itching and burning sensations, while also fostering the riephitelization of the anal mucosa.
-
Product Nail Rescuer & Nail Perfecting Lacquer
Nail Rescuer is a medical devices for the nails of hands and feet, aimed at treating and preventing the growth of fungi responsible for onychomycosis. It protects from aggression by external agents and promotes the nail restructuring process.It is available in 2 formats: single packaging and in a bipack (N...
-
Product OMACOR® MINI CAPSULES
(1) Hypertriglyceridemia; Hyperlipidemia
(2) Once daily, 2g or up to 4g if necessary
(3) Ideal package for administration of ESC recommended strength of Omega-3 (ESC: European Society of Cardiology)
(4) Easy to swallow, patient-friendly dosage form
-
Product Aciclovir 800 mg, 400 mg, 200 mg, Liposomal gel, Cream, Suspension
Type: OTC, Rx
Pharmaceutical form: Tablets, Liposomal topical Gel, Cream, Suspension
Active substance: Aciclovirum
...
-
Product Femasitol Plus
FEMASITOL 2.0 sachets, the new development Femasitol 2.0 contains an equal amount of myo-inositol to restore ovulation, optimize IVF procedures and prevent /manage gestational diabetes. The substitution of folic acid with 5-MTHF, the biologically active molecule, makes it possible to bypass MTHFR, and ...
-
Product Dolocalma (Metamizole magnesium capsules, 575 mg)
Dosage strength: 575 mg. Pharmaceutical form: capsule. Therapeutic indications: acute severe pain; severe spasmodic pain (biliary, kidney and lower urinary duct colic); high fever resistant to other antipyretic drugs; tumour pain.
...
-
Product Fenac-Gel (Diclofenac gel, 10 mg/g)
Dosage strength: 10 mg/g. Pharmaceutical form: gel. Therapeutic indications:
Anti-inflammatory and analgesic medicine, for external use, indicated for:
- post traumatic inflammation of tendons, ligaments and joints, due to sprains, luxations and bruises
- localised forms of...
-
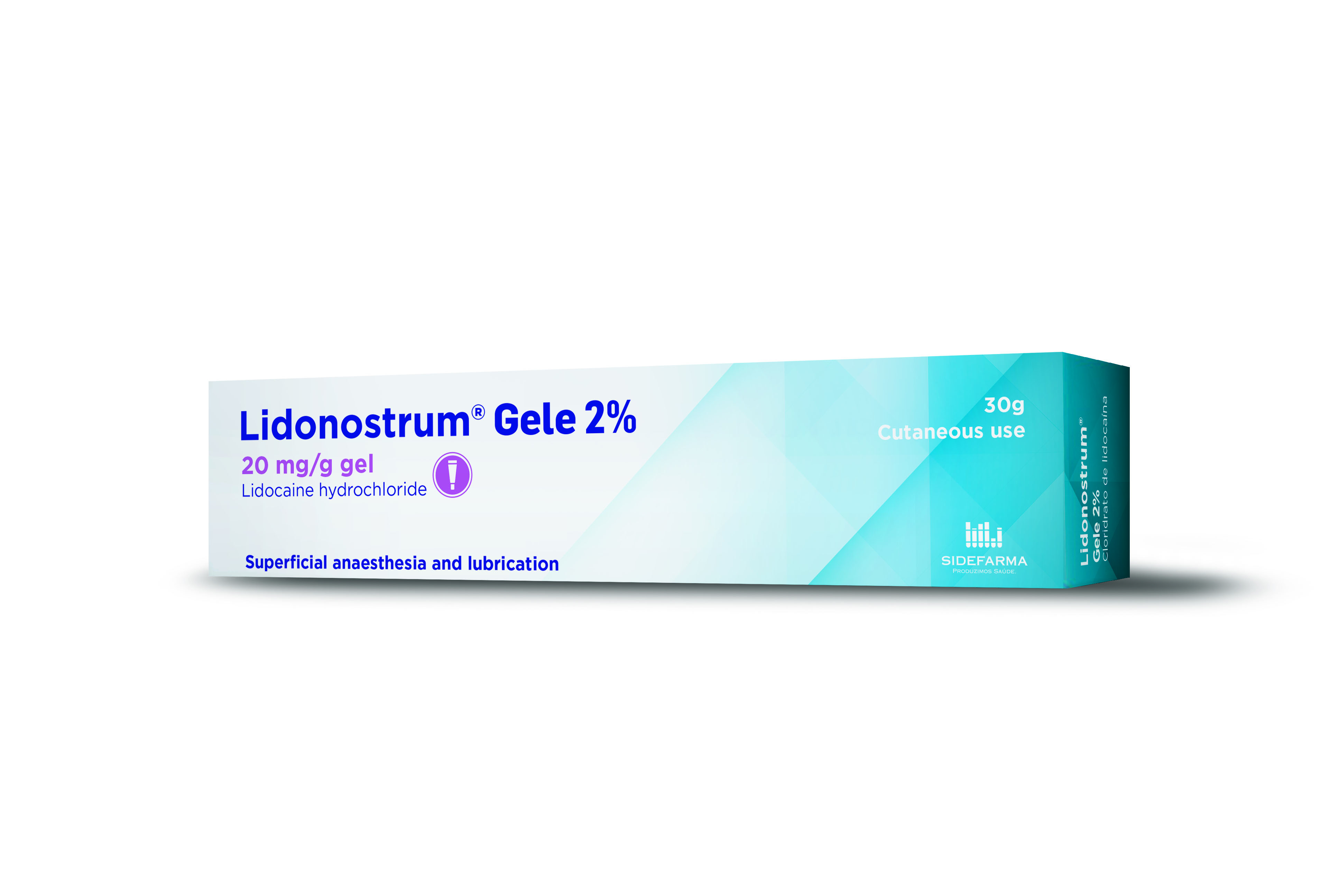
Product Lidonostrum Gele 2% (Lidocaine gel, 20 mg/g)
Dosage strength: 20 mg/g. Pharmaceutical form: gel. Therapeutic indications:
Superficial anaesthesia and lubrication:
- of the urethra: before cystoscopies, insertion of urinary catheter, urethral dilations or other endourethral procedures
- of nasal and pha...
-
Product Lidonostrum Bomba-Spray 10% (Lidocaine, cutaneous spray solution, 100 mg/ml)
Dosage strength: 100 mg/ml. Pharmaceutical form: cutaneous spray, solution. Therapeutic indications:
- Nasal procedures such as puncture of the maxillary sinus;
- Oral and dental procedures prior to injection;
- Oropharyngeal procedures such as gastrointestinal endoscopy;
- Procedur...
-
Product Rosazel
Treatment against rosacea and couperose disorders. A ultra-soothing cream gel, based on Hyaluronic Acid and Azeloglicina® which act synergistically to soothe and hydrate overactive skin. Rosazel is able to perform a filmogenic effect assuring protection from external aggression for an immediate skin relief...
-
Product Coripharma Dossier List
We offer out-licensing of our own developed dossiers, along with a range of services that enable our customers to take products to their respective markets at the date of patent expiry and under their own brand. Currently we have over 20 own developed dossiers on our pipeline and our dossier list is readil...
-
Product Pregnavie Complete
A nutritional supplement for pregnancy that holds all of the correct ingredients for mother and fetus in a one capsule a day format. Includes Omega 3 with a high concentration of DHA.
-
Product Enzymax Forte
A digestive nutraceutical with two studies against pharmaceutical alternatives (Valencia University, Cuban Cystic Fibrosis Commission).
Targeted Dual Release: The external capsule dissolves in the stomach, releasing digestive enzymes that are optimal in the acidic medium. The internal capsule ...
-
Product Cranbiotics
An innovative adjuvant therapy for urinary tract care: two products, one delivery. The external capsule contains cranberry and vitamin B complex and dissolves in the stomach. Helps to minimize bacterial adherence to the urinary tract epithelial cells and fight against vulvovaginal candidias...
-
Product Allopurinol
Dosage strength: 300 mg. Pharmaceutical form: tablet. Indications: • Gout treatment as well as primary and secondary hyperuricaemia due to renal impairment, neoplastic disease or its treatment. • It is also useful in the treatment of certain enzymatic disorders, such as Lesch-Nyhan syndrom...
-
Product GLA complex + Isoflavones + Oenothera biennis + Vitamin E
Food supplement containing GLA complex + Isoflavones + Oenothera biennis + Vitamin E. 30 LipidCaps in hard capsules of 600 mg. ...
-
Product Sulfadiazine
Dosage strength: 500 mg. Pharmaceutical form: tablet.Indications: • Treatment of infections such as urinary tract infections. • Prophylaxis of rheumatic fever in patients allergic to penicillin (not effective in the treatment of initial streptococcal infection). • Together with pyrimethamine,...
-
Product Ubidecarenone
Dosage strength: 30 mg. Pharmaceutical form: capsule. Indications: • Indicated in diseases where there is a deficiency of coenzyme Q10 such as mitochondrial cytopathies, namely cardiomyopathies and encephalopaties due to a deficit in electron transport chain (cell respiratory chain); • adjuvant in the tr...
-
Product Glimepiride
Dosage strength: 2 mg. Pharmaceutical form: tablets. Indications: • Treatment of type II diabetes mellitus that cannot be adequately controlled by diet, physical exercise and weight reduction. Contact us for more information!
-
Product Glimepiride
Dosage strength: 4 mg. Pharmaceutical form: tablet. Indications: • Treatment of type II diabetes mellitus that cannot be adequately controlled by diet, physical exercise and weight reduction. Contact us for more information.
-
Product Ginkgo biloba extract
Dosage strength: 40 mg/ml. Pharmaceutical form: oral solution.Indications: • Treatment of mild to moderate dementia. Contact us for more information!
-
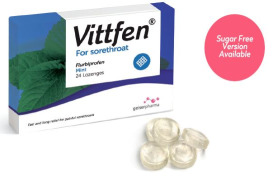
Product Lozenges - Flurbiprofen
• Active ingredient (s): 8.75 mg Flurbiprofen Flurbiprofen belongs to the group of medicines known as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) which are used to relive pain and inflammation. Flurbiprofen lozenges are used to reliev a painful or swollen sore throat. • Flavours (2): Mint •...
-
Product Lozenges - Benzydamine
• Active ingredient (s): 3 mg Benzydamine • Product Description: A locally-acting anti-inflammatory drug with local anaesthetic and analgesic properties for pain relief and anti-inflammatory treatment of inflammatory conditions of the mouth and throat. To be administrated three times a day. • ...
-
Product Carbocisteine Lysine
• Active Ingredient: 2.7 mg Carbocisteine • Product Description: Mucolytic that reduces the viscosity of sputum and can be used to relieve the symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD) and bronchiectasis by allowing the sufferer to bring up sputum more easily. • Unit size: 8 & 20 sac...
-
Product PENICILLIN V
• Active Ingredient(s): 50 mg/ml Penicilin V • Pharmaceutical Form: 60 ml/125ml/200 ml 100 ml under development • Indication: Antibiotic
-
Product Benzydamine Spray
• Active ingredient (s): 1.5/3.0 mg/ml Benzydamine Hydrochloride • Description: Sprayer for oral use indicated for symptomatictreatment of painful states of inflammation andswelling in the oropharyngeal space, such asinfections, laryngitis, mucositis from radiotherapyand other post-operative st...
-
Product Flurbiprofen Spray
• Active Ingredient (s): 8.75 mg/dose • Product Description: Sprayer for oral use indicated for symptomatic treatment of irritation and inflammation also associated with pain in the oral cavity (i.e. gingivitis, stomatitis, phayngitis) • Flavours: CherryTreatment of inflammation in sore throat. •...
-
Product Flurbiprofen lozenges sugar-free
• Active ingredient (s): 8.75 mg Flurbiprofen Flurbiprofen belongs to the group of medicines known as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) which are used to relive pain and inflammation. Flurbiprofen lozenges are used to reliev a painful or swollen sore throat. • Flavours (2): Honey&Lem...
-
Product DEXTROMETHORPHAN LOZENGES
• Active Ingredient(s)10 mg Dextromethorphan • Product Description: Cough suppressamt for the relieg of acute non-productive (dry,tickly) cough associated with respiratory track infection. • Flavours: Honey&Lemon • Unit size: 8,10,12,16,20&24
-
Product Spray with lidoaine
• Active Ingredient(s): 2.0 mg Lidocaine, 0,6 mg Amylmetacresol, 1.2 mg Dichlorobenzyl alcohol • Product Description: Sprayer for oral use indicated for the symtomatic relief of thoat infections, including severe sore throats. • Flavours: Peppermit • Unit size: 20ml • Marketing Authorisations Granted:...
-
Product Benzocaine and Chlorhexidine Gums
• Active Ingredient(s): 5 mg Benzocaine & 5 mg Chlorhexidine • Product Description: Local symptocatic relief of mild infections of the mouth and throat combined with pain and no fever. • Unit size: 12 gums • Primary Packaging: PVC/ALU blister 1x12 • Flavour: Mint
-
Product Dimenhidrinate Gums& Lozenges
• Active Ingredient(s): 20 mg Dimenhidrinate • Product Description: Prevention of motion sickness in adults and childen • Presentation: 24 lozenges/pack
-
Product Dimenhidrinate Solution
• Active Ingredients: 12,5 mg/5 ml Dimenhidrinate • Product Description: Prevention and treatment of symptoms associated with motion sickess (airsickness, seasickess, casickness) such as nausea, vomiting and/or vertigo in childern from 2 to 12 years. • Pharmaceutical form: Oral solution in sachet. ...
-
Product Ibuprofen Gel
• Active Ingredient(s): 50 mg/1 mg Ibuprofen • Product Description: Anti-inflammatory peinkiller gel applied to, and absobed though, the skin, indicated for symptocatic local relief and occasional rheumatic and muscular pains types, such as those produced by: minor bruises, blows, strains, torticoll...
-
Product Flurbiprofen Mouthwash
• Active Ingredient(s): 25 mg Flurbiprofen • Poduct Description: Symptomatic treatment of irritative-inflammatory conditions also associated with pain in the orogaringeal cavity for example (gingivitis, stomatitis, pharyngitis), also as a result of conservative or extractive dental therapy. &nb...
-
Product Flurbiprofen Stick
• Active Ingredient(s): 25 mg Flubiprofen • Presentation: Pack of 16 sticks of 10 ml each
-
Product Mercaptopurine 50 mg
• Indication: Purimmum is indicated fo the treatment of acurate promyelocytic leukemia (APL)/ acute myeloid leukemia M3 (AML M3) in adults, adolescents and children.
• Pharmaceutical Form: 6 mm yellowish tablets
-
Product Disulfiam Effervescent
• Active Ingredient: 200/400 mg Disulfiram • Indication: Treatment of chronic alcoholism • Pharmaceutical Fom: 50&100 effervescent tablets
-
Product Denture Adhesive Crea,
• Product Description: Fixative cream without parabens, zenk and flavour free. It prevents any pips and seeds getting stuck between the dentures and your gums. It expands to fill any gaps and blocks access to these bits of food, so you can enjoy a wider range of foods. The fixative will increase our abili...
-
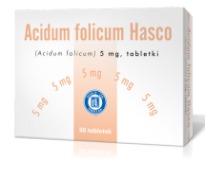
Product Acidum Folicum Hasco (5 mg, 15 mg)
Type: Medicinal product Pharmaceutical form: Tablets Package: 30, 60 and 90 tablets Category accessibility: Prescription medical Permit no 10273, 10272 Active substance:...
-
Product Tadalafil 2.5 - 5 - 10 - 20 mg - ODT in blister
Urology.ODT delivery form.
Available for outlicensing worldwide.
Contact us for more info.
-
Product Ibuprofen 200 mg - SOLUBLE GRANULES
Cold&Flu/PainkillerSoluble granules in sachet
available for outlicensing worldwide
Contact us for more info
-
Product Ibuprofen 400 mg - SOLUBLE GRANULES
Cold&Flu/PainkillerSoluble granules in sachet
Available for outlicensing worldwide
Contact us for more info
-
Product Acetylsalicylic acid 330 mg + Vitamin C 200 mg - EFFERVESCENT TABLETS
Cold&Flueffervescent tablets in tube
available for outlicensing worldwide
contact us for more info
-
Product Acetylsalicylic acid 400mg + Vitamin C 240 mg - EFFERVESCENT TABLETS
Cold&Flueffervescent tablets in tube
available for outlicensing worldwide
contact us for more info
-
Product Paracetamol + Pseudoephedrine 500 mg + 60 mg - EFFERVESCENT TABLETS/SOLUBLE GRANULES
Cold&Flueffervescent tablets in tube
soluble granules in stick
Avaialble for outlicensing worldwide
Contact us for more info
-
Product Paracetamol 500 mg+ Chlorphenamine 2mg + Vitamin C 250 mg - EFFERVESCENT TABLETS
Cold&Flueffervescent tablets in tube
available for outlicensing
contact us for more info
-
Product Calcium 1000mg + Vitamin D3 880 iu - EFFERVESCENT TABLETS/EFFERVESCENT GRANULES
Osteoporosiseffervescent tablets in tube
effervescent granules in sachet
available for outlicensing worldwide
contact us for more info
-
Product Ibuprofen 600 mg - SOLUBLE GRANULES
COld&Dlu/Painkillersoluble granules in sachets
Available for outlicensing worldwide
Contact us for more info
-
Product Paracetamol 1000 mg - SOLUBLE GRANULES
Cold&Flu/Painkillersoluble granules in sachet
effervescent tablets in tube
available for outlicensing worldwide
contact us for more info
-
Product Paracetamol 500mg + Codeine 30 mg - EFFERVESCENT TABLETS
Painkillereffervescent tablets in tube
available for outlicensing worldwide
contact us for more info

-
Product N-Acetylcysteine 600 mg - EFFERVESCENT TABLETS
Respiratory Systemeffervescent tablets
Available for outlicensing worldwide
Contact us for more info
-
Product N-Acetylcysteine 200 mg - EFFERVESCENT TABLETS
Respiratory systemeffervescent tablets in tube
Available for outlicensing worldwide
contact us for more info
-
Product Paracetamol 600mg + Phenyleprine HCl 10mg - ODG in stick
Cold & FluODG delivery form (stick pack).
Available for licensing out worldwide.
Contact us for more information

-
Product Climavit- Menopause
High quality food supplement based on botanicals - with clinical evidence on support.
The synergy of Genistein, Vitex Agnus Castus and Hawthorn helps hot flushing and nocturnal sweating mitigation as well as night time sleep quality.
Soluble Granules in sachet / ODG in stick
Available for ...
-
Product Lipidatin - Metabolic Syndrome
High quality food supplement based on botanicals - with clinical evidence on support.
The synergy of Red Yeast Rice, White Mulberry, Chomium and Banaba leads to a unique formulation with antidislipemic, hypoglicaemic and body weight management effect.
Soluble Granules in sachet
Available f...
-
Product Poligen Plus - PCOS Syndrome
High quality food supplement based on botanicals with clinical evidence on support.
The synergy of Myo-Inositol, D-chiro inositol, Cinnamon and Chromium is very promising in controlling the disorder of PCOS and Insulin Resistance.
Soluble Granules in sachet.
Available for outlicensing worl...
-
Product Memodiol - Memory Enhancing
High quality food supplement based on botanicals with bibliographic support.
Rhodiola and Melissa extracts in synergy with antioxidant vitamins and L-Acetylcarnitine prevent the impairment of memory and learning functions.
Soluble Granules in sachet
Available for outlicensing worldwide. qq...
-
Product Mindtonic - Cognitive functions
High quality food supplement based on botanicals with bibliographic support.
The synergy of antioxidan vitamins, including vitamin B and D, and Griffonia, source of tryptophan, Melatonin and L-Acetylcarnitine represent a specific protection of cognitive functions (oxidative damage).
Soluble G...
-
Product Macublue - Eye Health
High quality food supplement based on botanicals with bibliographic support.
Antioxidants, such as Lutein and Zeaxantine, in synergy with Saffron provide neuroprotectant action on visual health, improving retinal function and protecting from oxidative retinal stress (age related macular degeneration...
-
Product Metoclopramide 5mg - EFFERVESCENT TABLETS in strip
Gastrointestinal diseaseeffervescent tablets in strip
available for outlicensing worldwide
contact us for more info
-
Product OUTLICENSING
We out-license our registration dossiers, fully developed in house, for the partners to register and apply for a Marketing Authorisation in their country/-ies with their own trademark.
We are also willing to follow the registration procedure up to the granting of the Marketing Authorisati...
-
Product Papilocare
Gel for the prevention and adjuvant treatment of HPV-induced lesions:
· Medical Device Class IIa. Patented Vaginal Gel.
· Innovative & Unique (1st Treatment for HPV-dependent cervical low grade lesions)
· Target Patients: HPV+ and HPV+ with lesions (AS...
-
Product Palomacare
Palomacare is a 100% non hormonal medical device that moisturizes and repairs the vulvo-vaginal mucosa, re-balances the vaginal microbiota and improves vaginal health. It also improves the sexual intercourse. Compatible with condoms.
· Palomacare is indicated in those situations i...
-
Product Libicare
Libicare is a food suplement made from natural ingredients which have positive effects on improving the sexual function in women with low sexual desire.
· Unique dual effect (Promotes and improves the sexual desire and arousal)
· Complementary Intimate Gel Tube.
· Presentatio...
-
Product Pronolis
The first High Density (HD) Hyaluronic Acid gel: Complete and innovative range of viscosupplementation. Medical Device Class III
• High quantity of hyaluronic acid, up to 120mg per syringe • High concentration, for a fast and prolonged pain relief • Unique Mono-shot HD hyaluronic acid specificificall...
-
Product Digegluten
A nutritional supplement for gluten intolerance, that uses non-animal enzymes proven to break down proline-rich gluten in a one capsule per meal format. It also contains calcium, which contributes to the normal function of digestive enzymes.
-
Product INVIMA Approved Oncology
Lodaat's Oncology Colombian INVIMA approved injectables with CTD dossier
-
Product Butamirate Syr 7.5mg/5ml (200ml Bottle) (EU CTD Available)
Butamirate Syrup 7.5mg/5ml (200ml Bottle)
Reference Product: Sinecod ®/ NovartisDescription: Butamiratе Syrup is used for the symptomatic treatment of non-productive (dry) cough.
Dossier Status: EU CTD Available
Stability Studies: Zone II / Zone I...
-
Product Ertapenem Pd.C.So.In 1g/Vial (under development)
Ertapenem 1gPowder for concentrate for solution for infusion
Reference Product: Invanz® / MSD
Description: Ertapenem is a Carbapenem Antibiotic indicated in paediatric patients and in adults for the treatment of the following infections when caused by bacteria known or very likely to be susceptible t...
-
Product Linezolid Inj.Sol. 2mg/ml (300ml Plastic Bag) (EU CTD Available)
Linezolid 2mg/ml (300ml Plastic Bag) Solution for Infusion
Reference Product: Zyvoxid® / PFIZER
Description:Linezolid is a synthetic antibacterial agent that belongs to oxazolidinones. It has in vitro activity against aerobic Grampositive bacteria and anaerobic micro-organisms. Linezolid selectively ...
-
Product Meropenem Pd.I.S.Inf 500mg/Vial, 1g/Vial & 2g/Vial (EU CTD Available)
Meropenem 500mg, 1g, 2g / Vial Powder for Solution for Injection/Infusion
Reference Product: Meronem® / Astra Zeneca
Description: Meropenem is a penem antibacterial indicated for the treatment of: Complicated skin and skin structure infections (adult patients and pediatric patients 3 mo...
-
Product Imipenem + Cilastatin Pd.Sol.Inf (500+500)mg/Vial (EU CTD Available)
Imipenem + Cilastatin (500+500) mg/Vial Powder for Solution for Infusion
Reference Product: Primaxin® / Merck
Description: Imipenem + Cilastatin is a combination of imipenem, a penem antibacterial, and cilastatin, a renal dehydropeptidase inhibitor, indicated for the treatment of ...
-
Product Cefuroxime Pd.Inj.Sol 750mg/Vial & 1.5g/Vial (EU CTD Available)
Cefuroxime 750mg /Vial & 1.5g/Vial Powder for Solution for Injection
Reference Product: Zinadol® / GSK
Description: Cefuroxime is an antibiotic used to treat certain infections caused by bacteria, including respiratory-tract infections such as tonsillitis and pharyngitis (infections...
-
Product Esomeprazole Pd.I.S.Inf 40mg/Vial (EU CTD Available)
Esomeprazole 40 mg/Vial Powder for Solution for Injection/Infusion
Reference Product: Nexium® / Pfizer
Description: Esomeprazole is a proton pump inhibitor indicated for the treatment of the Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) with erosive esophagitis (EE) in adults and pediatric patients...
-
Product Ceftriaxone Ps.Inj.Sol 1g/Vial (IM, IV) (EU CTD Available)
Ceftriaxone 1g/Vial Powder for Solution for Injection/Infusion
Reference Product: Farcef® / Angelini
Description: Ceftriaxone is a cephalosporin antibacterial indicated for the treatment of the following infections caused by susceptible isolates of the desig...
-
Product Vancomycin Pd.Sol.Inf 500mg/Vial (EU CTD Available) & 1g/vial (EU CT Available: Q3 2021)
Vancomycin Vial Powder for Solution for Infusion
Reference Product: Voncon® / Lilly
Description: Vancomycin Hydrochloride is a glycopeptide antibacterial indicated in adult and pediatric patients (neonates and older) for the treatment of Septicemia, Infective Endocarditis, Ski...
-
Product Levofloxacin Sol.Inf 5mg/ml (100ml Bottle) (EU CTD Available)
Levofloxacin 5mg/ml (100ml Bottle) Solution for Infusion
Reference Product: Tavanic® / Sanofi
Description: Levofloxacin is used to treat infections of Lungs, in people with pneumonia, Urinary tract, including your kidneys or bladder, Prostate gland, where you have a long lasti...
-
Product Moxifloxacin Sol.Inf 400mg/250ml (250ml Bottle) (EU CTD Available)
Moxifloxacin 400mg/250ml (250ml Bottle) Solution for Infusion
Reference Product: Avelox® / BAYER
Description: Moxifloxacin, which belongs to a group of antibiotics called fluoroquinolones, works by killing bacteria that cause infections if they are caused by bacteria that are susceptible to Moxifloxa...
-
Product Brivaracetam Sol. Inf 10mg/ml (5ml Vial) (EU CTD Available: Q3 2022)
Brivaracetam 10mg/ml (5ml Vial) Solution for Injection/Infusion
Reference Product: Briviact® / UCB
Description: Brivaracetam is an antiepileptic agent which is indicated as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onsetseizures with or without secondary generalization in adults, adolescents and...
-
Product L-Carnitine Oral Solution 1g/10ml Vial (EU CTD Available)
L-Carnitine Oral Solution S.D. 1g/10ml Vial Oral Description: L-carnitine is a naturally occurring amino acid derivative present as a natural constituent in animal tissues, micro-organisms and plants. It helps the body produce energy and is important for heart and brain function, muscle movement, and ...
-
Product Palonosetron Inj.Sol. 250mcg/5ml (Vial) (EU CTD Available)
Palonosetron 250mcg/5ml (Vial) Solution for Injection
Reference Product: Aloxi® / Helsinn
Description: Palonosetron is an antiemetic and antinauseant agent belonging to serotonin (5HT3) antagonists category.
Palonosetron is indicated in adults and paediatric patients 1 month of age and older for t...
-
Product Sugammadex Inj.Sol. 100mg/ml (2 & 5 ml Vial) (EU CTD Available)
Sugammadex 100mg/ml (2 & 5 ml Vial) Solution for Injection
Reference Product: Bridion® / MSD
Description: Sugammadex is a modified gamma cyclodextrin which is a Selective Relaxant Binding Agent.
It forms a complex with the neuromuscular blocking agents rocuronium or vecuronium in plasma ...
-
Product Vildagliptin & Metformin Tabs (50+850 mg), (50+1000 mg) (EU CTD Available: Q3 2021)
Vildagliptin & Metformin(50+850 mg), (50+1000 mg) Film Coated Tablets Reference Product: Eucreas® / Novartis
Description: Vildagliptin & Metformin is a combination of 2 anti-diabetic agents indicated in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. More specifically, it is indicated...
-
Product Digoxin Inj.Sol. 0.25mg/ml (2ml Amp) (EU CTD Available)
Digoxin 0.25mg/ml Solution for Injection (2ml Amp)
Reference Product: Lanoxin® / GSK
Description: Digoxin is indicated in the management of chronic cardiac failure especially where cardiac failure is accompanied by atrial fibrillation, Supraventricular arrhythmias particularly ...
-
Product Somatostatin Ps.Sol.Inf. 3mg/Vial (EU CTD Available)
Somatostatin 3mg/Vial Powder for Solution for Infusion
Reference Product: Stilamin® / MSD Description: Somatostatin is indicated in cases of Growth Hormone Hypersecretion (ACROMEGALITY)
Dossier Status: EU CTD Available
Stability Studies: Zone II / Zone IVb
Shelf life (Origi...
-
Product Brivaracetam Oral Solution 10mg/ml (EU CTD Available: Q4 2022)
Brivaracetam 10mg/ml Oral Solution
Reference Product: Briviact® / UCB
Description: Brivaracetam is an antiepileptic agent which is indicated as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onsetseizures with or without secondary generalization in adults, adolescents and children from 4 year...
-
Product Lacosamide Oral Solution 10mg/ml (EU CTD Available: Q2 2022)
Lacosamide 10mg/ml Oral Solution
Reference Product: Vimpat® / UCB Description: Lacosamide is a functionalised amino acid which belongs to the group of antiepileptics. Lacosamide is used as monotherapy and adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial-onset seizures with or without secondary...
-
Product Lacosamide Solution for Infusion 10mg/ml (EU CTD Available: Q2 2021)
Lacosamide 10mg/ml Solution for Infusion
Reference Product: Vimpat® / UCB Description: Lacosamide is a functionalised amino acid which belongs to the group of antiepileptics. In vitro electrophysiological studies have shown that lacosamide selectively enhances slow inactivation of voltage-gated s...
-
Product Clindamycin Solution for Injection 150mg/ml (EU CTD Available: 2022)
Clindamycin 150mg/ml Solution for Injection (2ml & 4ml amps) Dalacin® / PfizerDescription: Antibacterial. Serious infections caused by susceptible Gram-positive organisms, staphylococci (both penicillinase- and non-penicillinase-producing), streptococci (except Streptococcus faecalis) ...
-
Product Apixaban F.C. Tabs 2.5mg/tab & 5mg/tab (under development)
Apixaban Film Coated Tablets 2.5mg & 5mg
Reference Product: Eliquis® / Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer
Description: Prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in adult patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF), with one or more risk factors, such as prior stroke or transie...
-
Product Ceftaroline Fosamil Pd.C.So.In 600mg/Vial (under development)
Ceftaroline Fosamil Powder for Concentrate for Solution for Infusion 600mg/vial
Reference Product: Zinforo® / Pfizer
Description: For the treatment of the following infections in neonates, infants, children, adolescents and adults, Complicated skin and soft tissue infections (cSSTI),&...
-
Product NUROM
NUROM, is a combination of natural elements, based on Alpha-Lipoic acid, Carnosine, Zinc and Vitamin B with clinical trials showing efficacy in the prevention and treatment of (diabetic) neuropathy. NUROM can also be used in Peripheral Neuropathies: due to compression, trauma, inflammation, resulting i...
-
Product Retinol
Dosage strength: 50.000 UI. Pharmaceutical form: capsule.Indications: • Treatment of vitamin A deficiency that can present throughout symptoms such as xerophthalmia, keratomalacia, changes in night vision, dryness of the skin and hyperkeratosis, reduced resistance to infections. • The medicine can a...
-
Product Zyfort
Indications
Neuralgia, polyneuritis, facial paresis, ischialgia, Vit. B deficiency
Each ZYFORT ampoule contains:
Thiamine HCl ……………100 mg
Pyridoxine HCl ………….100 mg
Cyanocobalamine …...5000 mcg
Package : Box of 20 ampoules @ 3 ml

-
Product Destavell
Indications
Allergic Rhinitis: Destavell tablet 5 mg are indicated for the relief of the nasal and non-nasal symptoms of allergic rhinitis (seasonal and perennial) in patients 12 years of age and older. Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria: Destavell tablets are indicated for the symptomatic relief of prur...
-
Product Panvell enteric coated tablet
Contains Pantoprazole 40 mg
Indication:
In combination with the appropriate antibiotics for eradication for Helicobacter pylori in patient with peptic ulcers with the objective of reducing the recurrence of duodenal and gastric ulcer caused by this microorganism.
Duodenal ulcer
Ga...
-
Product Prostam SR
Indications:
Lower urinary tract symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia
Each Prostam SR contains Tamsulosin 0.4 mg
Package: Box of 30 sustained-release tablets

-
Product Angintriz MR
Indications
Adjunctive to established anti-anginal therapy. Should not be used as monotherapy
Each ANGINTRIZ MR contains Trimetazidine dihydrochloride 35 mg
Package : Box of 3 strips of 10 modified release film-coated tablets

-
Product Kalquest
Indications
Hyperkalemia due to acute and chronic renal failure.
Contains Calcium Polystyrene Sulphonate 5 g
Package: Box of 30 sachets @ 5 g

-
Product Novellmycin
Indications
Infection caused by gram positive and gram negative bacteria.
Such as urinary tract infections, Osteomyelitis, Meningitis, ear infection, peritonitis, diabetic foot infection, prophylaxis
There are 2 strengths available:
- Fosfomycin.............................1G
- Fosfo...
-
Product Osflex
Indications:
Deformative knee Osteoarthritis & shoulder periarthritis.
Osflex contains Sodium Hyaluronate 25 mg/2.5 ml
Package : Box of 1 syringe of 2.5 ml

-
Product Pure Baby Rash Cream
Indications
Overcome and protects baby's sensitive skin from nappy redness, nappy rash, and keeps baby's skin soft.
Pure Baby Rash Cream contains:
D-Panthenol..........................5%
Zinc oxide..............................10%
Package : Box, tube 50 gr.

-
Product Pure Baby Diaper Cream
Indications
Helps prevent baby's skin from mild irritation and rashes.
Pure Baby Diaper Cream contains:
- Zinc oxide.
- Castor oil.
- Sunflower oil.
Package : Box of 1 tube of 100gr; Box of 1 tube of 200 gr

-
Product Pure Baby Lotion
Indications
Maintain soften and moisture baby’s skin with moisturizer extract from natural source
Pure Baby Lotion contains:
- Sun flower seed oil.
- panthenol
- theobroma cacao seed butter
- tocotrienols
- aloe barbadensis leaf juice
Package : Bottle of 80 ml ...
-
Product Pure Baby Soothing Cream
Indications
Daily use to soften and moisture baby's sensitive skin
Pure Baby Soothing Cream contains :
- Sun flower seed oil.
- Avena sativa extract
- Avena sativa flour
- Hydrolyzed oat protein
- Hydrolyzed olive leaf extract
Package : Tube of 100 gr and 20...
-
Product Pure Baby Sun Block
Indications
Provide sun protection for baby's skin
Pure Baby Sunblock contains:
- Zinc oxide micronized particle.
- Natural moisturizer apricot kernel oil.
- Vitamin E
There is no PABA (Para Amino Benzoic Acid) in Pure Baby Sunblock.
Package : Tube of 50 gr, 100 g...
-
Product PureKids Inhalant Decongestant Oil
Indications
To help relieving nasal congestion and respiratory relief.
Purekids Inhalant Decongestant Oil contains natural extract from: Eucalyptus oil, Cajuput oil, Clove oil, Juniperberry oil, Levomenthol, Dementholized mint oil, Methyl salicylate.
Package : Box of 1...
-
Product FEMAFERTI gel
FEMAFERTI GEL, a medical device Class IIa based on sugars, mineral salts, creatine, carnitine, Hyaluronic acid and Lactic acid. It creates an optimal invironment for spermatozoa, assistsmaintaining a suitable pH for natural conception and is characterized by seminal fluid-compatibleosmolality. The efficacy...
-
Product medEctoin Dermatitis Cream
Medical device for symptomatic treatment and relief of various types of inflammatory dermatoses. • Helps to relieve and calm irritated and damaged skin by reducing inflammatory reactions and supporting the regeneration process • Reduces dryness by increasing skin moisture content and therefore smoothen...
-
Product medEctoin Lozenges
Medical device for treatment and prevention of common cold symtoms, dry mouth and throat, and hoarseness. • Reduces symptoms of acute Pharyngitis, such as hoarseness, sore throat, and pain on swallowing • Reduces inflammations and stabilizes the mucous membranes in mouth and throat • Soothes irrit...
-
Product medEctoin Mouth & Throat Spray
Medical device for treatment of dry and irritated epithelia in mouth & throat. • Reduces symptoms of acute Pharyngitis and/or Laryngitis, such as sore throat, hoarseness, cough, and pain on swallowing • Reduces the duration of a sore throat/hoarseness • Relieves first symptoms such as hoarse...
-
Product MUCONIS sachets
MUCONIS sachets is a food supplement based on N-acetylcysteine, Enzymes from fermented maltodextrins, Riboflavin and Vitamin C indicated in respiratory diseases with viscous hypersecretion, respiratory diseases with painful inflammation and respiratory diseases with bacterial infection as it fluidifies...
-
Product MUCONIS nasal spray
MUCONIS nasal spray is a medical device Class IIa based on N-acetylcysteine and Chloride which facilitates the fluidification and mechanical removal of mucus and/or mucopurulent secretions stagnant inside the nasal cavity and inside the paranasal sinuses. It acts by fluidifying the mucus through the ph...
-
Product VINERGIZE oral vials
VINERGIZE oral vials is a food supplement composed of cold liver oil, vitamins A, B1, D, E, pollen,royal jelly, glycine and Zinc. Royal jelly, vitamin D and glycine present restorative properties. Royaljelly is rich in essential amino acids, easily assimilable vitamins and minerals this is why roya...
-
Product RESTOGYN-T tablets
RESTOGYN-T vaginal tablets is a medical device based on Tyndallized Lactobacillus, Natural (Hydrolyzed/ Femented) Mix Milk Protein, Lactic acid and Fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS). The combined action of the components of Mivagyn T vaginal tabs restores the vaginal bacterial flora and pH reducing burning,...
-
Product GASTIROM MAG Oral emulsion
GASTIROM Mag oral emulsion is a medical device Class IIa based on low molecular weight Hyaluronic Acid, Magnesium Alginate, Myrrh extract and Simethicone, useful for those patients that chronically suffer symptoms linked to the gastroesophageal reflux disease and need an extra-strong long-lasting rel...
-
Product MICRONORM drops
ICRONORM drops is a is a food supplement based on Lactobacillus Reuteri able to support the balance of intestinal flora. Micronorm can be used in infants and children; it can be used in combination with the use of antibiotics and during diarrheal episodes.
-
Product GASTUSEN oral gel
GASTUSEN oral gel in stickpacks is a medical device Class IIa based on low molecular weight Hyaluronic Acid, Magnesium Alginate and Myrrh extract, useful for those patients that occasionally suffer symptoms linked to the gastroesophageal reflux disease (mild GERD for patients who experience mild symp...
-
Product ENGIA vials
ENGIA vials contain fresh royal jelly, vitamin B complex (B1, B2, B5, B6), vitamin D3, vitamin PP, vitamin C, iron, and glutamine. It is useful as a metabolic and energetic stimulus, helps to improve concentration and cognitive functions and relieves sensations due to stress and fatigue. The efficacy ...
-
Product Out Licensing Dossiers
• Out Licensing • Technology Transfer • Co-Development / Profit Sharing with •
Technology Partners
API partners
Marketing Partners
CMO Partners

-
Product Tiroxil ® D
A healthy thyroid for the 50+ generationDietary supplement to support thyroid function in people over 50 years old.
• Pharmaceutical form: Tablets • Clinical trials: Strong scientific background supports inclusion of vitamin D to the Tiroxil 4.0 formulation to support patients over 50....
-
Product Inofolic ® & Inofolic ® HP
A breakthrough in the managementof PCOS and female infertility
• Pharmaceutical form: Sachets | Soft-gel caps • Clinical trials: Efficacy of the product line is supported by 60+ international clinical trials in more than 5000 patients. Many published studies demonstrate efficacy in imp...
-
Product Inofolic® Combi and Combi HP
40:1 The Perfect BalanceA High Performance dietary supplement for the managementof PCOS, especially in overweight and obese women. • Pharmaceutical form: Soft-gel caps • Clinical trials: The efficacy of this innovative formulation, with the ideal ratio of myo-inositol and D-chiro-inositol has be...
-
Product Inofolic® Combi HP
- Dietary supplement for PCOS management,especially in overweight and obese women.- Pharmaceutical form: soft gel caps.- The innovative formulation efficacy has been confirmed by clinical trials, recent sophisticated in vitro study and reviews published on high Impact Factor scientific journals.
- Inter...
-
Product Inofolic® Plus
For women seeking pregnancy or undergoingAssisted Reproductive Technology (ART)Dietary supplement for women to improve oocyte and embryo quality.
• Pharmaceutical form: Soft-gel caps • Clinical trials: Clinical efficacy is demonstrated in 4 clinical trials and confirmed in a number o...
-
Product Inofolic® Luteal
Dietary supplement for women to enhance implantation rate,improving endometrial receptivity. It supports the correct evolutionof gestation, especially in the first trimester.
• Pharmaceutical form: Soft-gel caps • Clinical trials: Two published clinical trials support safety and effica...
Like every other company, pharmaceutical companies need a marketing strategy to make new drugs and drug products accessible at a local, national, and global level. In recent years, out-licensing has quickly become an important and well-recognized marketing strategy in the global pharmaceutical sector. More pharmaceutical companies have turned to out-licensing given the increasing cost of drug development, marketing, and competition. Drugs, brand names, and research products are being out-licensed for production completion or marketing.
Pharmaceutical companies use out-licensing to find partnership(s) that will enable them to get in-house developed drugs, drug products, or research products to the target audience. Out-licensing creates an opportunity for companies to develop or boost their portfolio and gain massive and rapid ROI. These companies may partner with marketing companies, legal firms, and even another pharmaceutical company to achieve this. Here, we will carefully examine out-licensing, its purpose, how it works, and its benefits to pharmaceutical companies and the global pharmaceutical sector as a whole.
What is out-licensing?
Out-licensing refers to the sales of the rights to a fully or partially developed or potential drug or drug product, brand name, etc., to a marketing firm or another pharmaceutical company (third party) for marketing or further development and production. This process usually involves two or more parties (pharmaceutical companies, marketing firms, etc.). In out-licensing, the innovator (licensor) transfers its right to intellectual property to a third party (licensee) for manufacturing, development, or marketing within a particular geography for an agreed period, which is renewable. The licensee is expected to pay a royalty or license fee for the licensed product based on mutual agreement between the two parties. This process entails certain legal actions and processes that ensure patent protection.
How does out-licensing work?
The out-licensing process is a well-thought-out process and is expected to yield positive results if followed carefully. In most cases, out-licensing is carried out by small and mid-sized pharmaceutical companies because of a lack of funds or the capacity to handle the production, clinical trials, or marketing process. These companies set out marketing departments or outsourcing firms to identify potential in-licensing companies and opportunities and carry out the out-licensing process.
The steps involved in out-licensing include lead generation, shortlisting (based on specific areas such as dosage form, therapy focus, etc.), one-sheet document creation, approach, and connection to the target company, presentation of information memorandum (IM) or Non-confidential Information Package (NCIP), NDA or CDA signing, Presentation and Collection of business proposals, Signing and exchange of term sheet, exchange of relevant data, final agreements, payment of fees depending on the contractual agreement.
This process primarily involves searching for partnership (s) with an in-licensing company or firm to assist in product manufacturing, development, production, sales, or marketing. The licensor and the licensee have a mutual agreement on the development or commercialization of the drug, patent, brand, or technology in exchange for a one-time payment, upfront fee, milestone payment, or payment of royalties upon completing a specific development or commercialization steps. These agreements operate on a quid pro quo basis. Most pharmaceutical companies tend to opt for payment plans that include recurring payment of fees.
What is an example of out-licensing?
Over the years, several large, mid-level, and small pharmaceutical and biotech companies have adapted to out-licensing to cut development investments and increase returns on investments. Many pharmaceutical companies have gone into out-licensing deals to partake in its benefits.
A commendable out-licensing example is the Ortho biotech and Millennium Pharmaceutical Velcade out-licensing deal. MLNM’s Velcade, which was approved for the treatment of multiple myeloma in the US, was out-licensed to Ortho biotech. This out-license deal was made with a $15-million upfront payment and a milestone deal of $750-million, with 75% of this payment coming from oncological applications.
What is the difference between a license and a contract?
Although a license and a contract may be made for similar reasons, they are quite different. In contract manufacturing or contract agreements, the innovator or seller continues to maintain exclusive rights to the intellectual property and pays for the manufacturing, development, or marketing process. Here, the contracted manufacturer holds no rights over the assets. On the other hand, in-licensing, the licensor, seller, or innovator's hands or sells the right to the intellectual property to the licensee or partnering firm and is paid a licensing or royalty fee based on the agreement made. However, note that the licensor maintains right over the innovative products, which can be lost in the agreement cycle or product life cycle.
Pros and cons of out-licensing
A licensing agreement gives the licensee or partnering company rights to use, manufacture, develop, or sell an intellectual product (drug, brand, patent, technology, etc.) owned by the licensor or innovator. The rights to be given are outlined, reviewed, and signed by both parties. The type and extent of rights leased or sold are usually dependent on the licensing agreement's purpose.
Out-licensing provides several advantages and disadvantages to both the licensor and licensee. It is paramount that these advantages and disadvantages are considered before final agreements are made.
What are the pros of out-licensing?
Out-licensing provides the licensor and licensee with many benefits. With the increasing cost of drug or drug product manufacturing, development, clinical trials, and commercialization, out-licensing has become a go-to option for various pharmaceutical companies. By out-licensing, licensors reduce the financial burden of manufacturing, production, or commercialization of patents and create a source of passive income and revenue. In license agreements, the licensor retains ownership of the intellectual property asset while also receiving royalty income from it.
The recurring payments received from the licensing agreements are highly beneficial to the licensor and also the licensee. Pharma companies can use out-licensing to gain access to new or foreign markets and enlarge their portfolios. Licensees with threatened market positions from competitor companies can also benefit from this by introducing new products into the market. The licensor and licensee also experience a reduced risk of business development.
What are two possible risks involved with out-licensing?
As with every other marketing or business development strategy, out-licensing comes with many risks. Although these risks are avoidable, they are inevitable and may be detrimental to both parties. Out-licensing or licensing agreements put the licensor, innovator, or seller at risk of losing complete or partial rights to the intellectual property. Loss of intellectual property right is the greatest risk associated with this process. Given the nature of licensing agreements, the licensor is dependent on the skills and resources of the licensee for the generation of revenue. However, there may be a loss of or no revenue generated if the licensee is ineffective or incompetent. This is even more devastating in the case of an exclusive license.
What are the cons of out-licensing?
Licensing agreements or out-licensing also present the licensor and licensee with various disadvantages. The out-licensing deals involve partnership and relationships with individuals, and as a result, interpersonal and -company/community conflicts are inevitable. Out-licensing gives room for intellectual property theft, misuse, and piracy. Problems with the development, manufacturing, or commercialization process can leave a dent in both licensor and the licensee's reputation. For example, the production of poor-quality drugs such as synthetic vaccines can greatly affect the reputation of both companies.
Also, revenue generation is not guaranteed as sales may or may not be made, and this is dependent on various factors. Royalty fees aren't always instant and may take a while to arrive based on sales made. Finally, due to a lack of transparency and integrity, licensees may be at the risk of royalty litigation. Royalty litigation incurs high costs of legal action on the licensor.
Best Uses for the out-licensing processes
There are several reasons why companies consider out-licensing processes, and they differ from one company to another. However, two uses are uniform among all the companies that consider the out-licensing processes. The first is to build strategic partnerships with other companies that have a wider reach. Strategic partnerships are the foundation upon which many of the big pharmaceutical companies we know today thrive. Once a company studies the market and finds out that owning a drug's license will limit its market share, they consider out-licensing. With the processes involved, drug companies can grow to leverage companies' brand quality they are out-licensing to.
Another use of the out-licensing process is to get a particular product in the right hand. It is one thing to engage a good marketing strategy; it is another for such a strategy to yield the desired results. Using the out-licensing processes can help a company reach its target audience faster and better and get its products to the right hands.
What are the best uses for the out-licensing process?
If you own a drug company and you are considering the out-licensing process, the best use of it for you will be in the area of finance. While the financial relationship involved in out-licensing differs from that involved in other licensing types, it can yield a lot of financial return. Knowing the right company to grant the license to, the best time to do so, and documentation of the process are the best ways to go about the out-licensing process.
Where can you find out more about out-licensing?
Out-licensing is a precise and popular process, not just in the pharmaceutical sector but also in every other business sector. Business owners can gather more information on outsourcing from the internet, the licensor, marketing firms, and outsourcing firms. These platforms give a detailed explanation and understanding of out-licensing, the processes involved, benefits, drawbacks, and examples of out-licensing. Also, to make the learning process easier, many online courses concerning out-licensing are available on different e-learning platforms. E-learning platforms such as Informaconnect, eDx, Alison, etc., have made simple courses available to interested individuals.
How do companies use out-licensing to their advantage?
Not all companies can reach out to their target audience as much as they want to. Even with a good marketing strategy, there are prospects that the company may not reach. This is where out-licensing comes to play and how pharmaceutical companies use it to their advantage. By out-licensing a drug, a company studies the market for players with an extensive reach. These players have the audience but do not have the drugs. Companies their give license to such players and, in turn, make a handsome profit from it. In doing this, pharmaceutical companies make sure to sort all the legal paperwork that secures the out-licensing process and strict payment of licensing fees.
How to out-license your company’s drug
Drugs, drug products, patents, etc., all follow a basic out-licensing process to establish a licensing agreement. However, although the primary process remains the same for all intellectual properties, there are a few differences in follow-up or prior processes carried out.
How do you out-license your brand name?
Once your brand name's value or potential is recognized within a particular niche, locally, nationally, or globally, it can be used as a strategic means for brand growth, push a new product into the market, etc. In brand licensing, you lease or sell the rights to your brand name, logo, or intellectual property to a partnering company to use their products. The leased brand is used within a specified time and for specific purposes based on the two companies' contractual agreement. The licensor is then paid a financial remuneration for the intellectual property leased.
The steps involved in out-licensing include building and establishing your brand name, establishing licensing guidelines, licensing to trusted companies, limiting licensing extensions, implementing license training to ensure the manufacturing or production of quality products, and monitoring brand reputation as concerned with the use of licensed products. These are essential additional steps taken when leasing your brand name to a licensee.
How do you out-license your company’s drug?
The process of out-licensing your company's drug starts with identifying a company that requires permission to use your drug or drug product. It also includes the process of drafting a licensing agreement that suits both parties. Where you produce the drug but lack the resources to market it effectively, it is best that you find a larger pharmaceutical firm and license them. By doing so, you are giving them the approval needed to either complete the drug's production process, market it, or do both. Also, this licensing could give approval to run a drug test, alcohol test, or access to any of the other random drug testing procedures.
What are some of the drawbacks of the out-licensing process?
Finding the right licensee for the out-licensing is difficult and may be prolonged. Another drawback is the possible misuse when it is a sensitive product like marijuana. Substance abuse remains one of the major drawbacks of out-licensing. Brand names, patents, drugs, and drug products, will stand a better chance at success if the right licensee is found and the license agreement, well structured. Although this process is beneficial and has been used by various pharmaceutical companies globally, it has some drawbacks that may significantly affect the process's success.
A few of these include the risk of complete or partial loss of control or right over the innovative product, royalty litigation, poor marketing strategy and execution, IP theft, and many others. There is also the possibility of a testing program or inability to reach a potential license application agreement. These downsides are significant causes of concern that are likely to impact the result of this process.
References
https://brandway.com/en-4/ways4brands/brand-out-licensing/?cookie-state-change=1609967154938
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/pharma-inout-licensing-framework-approach-model-factors-gain
https://www.intracen.org/What-are-the-advantages-and-disadvantages-of-licensing2/
https://brandongaille.com/14-licensing-advantages-and-disadvantages/
https://www.expresspharma.in/management-pharma/pharma-licensing-framework-and-the-way-forward/
References
Upcoming Events
-
CPHI Middle East 2024
Riyadh Front Exhibition & Convention Center Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
10 Dec 2024 - 12 Dec 2024 -
Pharmapack Europe 2025
Paris Expo, Porte de Versailles - Hall 7.2 | Paris, France
22 Jan 2025 - 23 Jan 2025 -
CPHI Japan 2025
East Halls 4, 5 & 6, Tokyo Big Sight, Tokyo, Japan
09 Apr 2025 – 11 Apr 2025
Pharmaceutical Industry Webinars
-
Webinar Leveraging Real-Time Clinical Data to Deliver Certainty in Solubility Enhancement and Modified Release Development
-
12th December 2024
-
3pm BST/ 4pm CET
-
-
Webinar The CPHI Sustainability Collective: A New Initiative to Support a Sustainable Pharma Value Chain
-
10th December 2024
-
3pm BST /4pm CET
-
-
Webinar Key to Success: A CDMO's Pathway to Biologics Excellence
-
5th November 2024
-
3pm BST/ 4pm CET
-
-
Webinar The Changing Dynamics of Global API Manufacturing
-
17th September 2024
-
3pm BST/ 4pm CET
-
-
Webinar Shaping the Future of Italy’s Pharma Market: Trends and Opportunities
-
4th September 2024
-
4pm CET/ 10am EST
-
-
Webinar Fragment-Based Oligonucleotide and Oligopeptide Synthesis
-
30th Jul 2023
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
-
Webinar GMP Rationale for Sterile High-Potency/Toxic Pharmaceuticals
-
18th June 2024
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
-
Webinar Unlocking Opportunities in the Growing Pharma Landscape of The Middle East
-
5th June 2024
-
3pm CET / 9am EST
-
-
Webinar Exploring Technological Trends in the Future of Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
-
23rd May 2024
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
-
Webinar Achieving Manufacturing Excellence Through Digital Transformation
-
16th April 2024
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
-
Webinar Made in Africa: What’s Driving Pharma Manufacturing
-
28th March 2024
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
-
Webinar Case Study: Risk Management for Annex 1 Sterile Production EMS
-
28th February 2024
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
-
Webinar Innovative Strategies for B2B Pharma Marketeers: Driving Value through Content
-
20th February 2024
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
-
Webinar Revolutionizing Pharma: Data and AI Unleashed
-
18th January 2024
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
-
Webinar Optimal Temperature: Elevating Biologics Cold Chain Excellence
-
16th January 2024
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
-
Webinar Market Outlook – The Biggest Pharma Trends of 2024
-
12th December 2023
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
-
Webinar The Next Frontier – Emerging Opportunities in the LATAM Pharma Market
-
21st November 2023
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
-
Webinar Vistamaxx™ MED - imagine the possibilities for healthcare product performance
-
10th October, 2023
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
Position your company at the heart of the global Pharma industry with a CPHI Online membership
-
Your products and solutions visible to thousands of visitors within the largest Pharma marketplace
-
Generate high-quality, engaged leads for your business, all year round
-
Promote your business as the industry’s thought-leader by hosting your reports, brochures and videos within your profile
-
Your company’s profile boosted at all participating CPHI events
-
An easy-to-use platform with a detailed dashboard showing your leads and performance

































































































































































































.jpg)
















.png)






.png)

.png)



.jpg)


