CPHI Online is the largest global marketplace in the pharma ingredients industry
-
Products551,744
-
Companies7,781
-
Articles11,636
-
Events8
-
Webinars342
Excipients
Excipients Companies (216)
Excipients News
-
News What can you expect from CPHI Milan 2024?
CPHI Milan 2024 marks the 35th anniversary of CPHI. The 35th Edition of the show, taking place 8–10 October, promises to be a celebration of everything pharma, covering every sector, and featuring thought leaders and trailblazers shaking up the i...25 Jul 2024 -
News How are new PFAS regulations impacting excipient manufacture? – CPHI North America Interview
In another interview from CPHI North America in Philadelphia in May, Peter Schmitt from Montesino Associates talks about his presentation on 'Navigating the Waters of Change: The Impact of New PFAS Regulations on the Manufacture of Excipients ...4 Jul 2024 -
News The CPHI North America agenda - see what's in store
CPHI North America will once again be held in Philadelphia this May. Philadelphia has been home to CPHI North America for several years and continues to be a hub for the US pharmaceutical market.21 Mar 2024 -
News CPHI Podcast Series: What to expect from novel excipients?
In this month's episode of the CPHI Podcast Series, Digital Editor Lucy Chard is joined by Nick DiFranco, the Global Market Manager for Novel Pharmaceutical Excipients at Lubrizol Life Science to discuss the ins and outs of excipients, how the...29 Feb 2024 -
News galenIQ: a brand of Beneo
The number one provider for medicated lozenges. Hard-boiled lozenges with galenIQTM 900 - the sweet filler-binder.23 Aug 2023 -
News Roquette expands plant-based excipient portfolio with Crest Cellulose acquisition
Crest Cellulose, an Indian excipient manufacturer, has been acquired by plant-based pharmaceutical excipient provider Roquette in a bid to increase the latter’s presence in the Asia Pacific region.4 Oct 2022 -
News Dr. Paul Lohmann® - Your Partner for high value Mineral Salts
With our expertise in the chemical and physical modification of Minerals and our customer-oriented philosophy, we are the ideal partner to turn your ideas into reality. Meet us at CPHI stand #110F50!27 Sep 2022 -
News Accepting novel excipients for innovative drug development
With the rapid development and manufacturing of new drugs and therapeutics being pushed through the pipeline, excipient manufacturers are navigating a challenging landscape to meet the demand for new and novel excipients.30 Aug 2022 -
News CPHI Podcast Series: The importance of novel excipients for innovative drug development
The latest episode in the CPHI Podcast Series dives into the world of novel excipients and explores their importance for innovative drug development.2 Aug 2022 -
News Hovione and Zerion Pharma collaborate to commercialise low drug solubility solution
By joining forces, the two companies will be able to bring Dispersome to the market faster for novel drug development22 Feb 2022 -
Sponsored Content Croda: Solutions for Your High Value Drug Products
Formulating a drug for parenteral delivery comes with its fair set of challenges. Aside from a high level of sensitivity to external factors like light and heat exposure, these large and complex drugs are prone to degradation when exposed to various ch...11 Feb 2022 -
News UPDATED: COVID-19 Vaccine and Therapeutic Development Tracker
The latest coronavirus updates and developments impacting the global pharmaceutical supply chain. Includes the latest news surrounding the therapeutic developments, updates to vaccines and boosters, and the global pharmaceutical regulations that need t...28 Jun 2024 -
News Roquette to advance drug delivery research with new US Innovation Center
The new facility will focus on the research of excipients for oral dosage forms, drug delivery systems, nutraceutical APIs and innovative pharma ingredients14 Dec 2021 -
News CPHI releases Pharma Trends 2022 report
CPHI has launched its forward-looking pharma trend report for 2022 and it is now available to read on CPHI Online.6 Dec 2021 -
News CPHI Podcast Series: Annual Report 2021 Roundtable
In this special edition podcast, Informa Markets pharma editor Gareth Carpenter speaks to Bikash Chatterjee, CEO at Pharmatech Associates and Dan Stanton, Editor and Founder at BioProcess International about some of the findings in the recently pu...23 Nov 2021 -
News CPHI Worldwide is back, and this time it’s hybrid
A new in-person and online edition of CPHI Worldwide, transforming your event experience.1 Nov 2021 -
Sponsored Content CPHI Webinar: Develop ODTs in a FLASH with UltraBurst™ - Watch On Demand
Catch up on the latest trends and developments in orally disintegrating tablet (ODT) formulation development30 Sep 2021 -
Sponsored Content IFF Pharma Solutions: Paving the Way for Superior Suspensions
Shawn Branning, Global Strategic Marketing Manager at IFF – Pharma Solutions30 Sep 2021 -
News The Top Ten CPHI Discover Company Showcases
CPHI Discover (May 17-28) gave Pharma companies, suppliers and service providers the opportunity to keep potential buyers and partners abreast of the latest news, product information and market trends in the form of free-to-access, downloadable content...3 Jun 2021 -
News COVID-19 Pharma Development Tracker
The latest coronavirus updates and developments impacting the global pharmaceutical supply chain (continued from here)31 May 2021
Excipients Products (500+)
-
Product Excipients for Gel Capsules
Enhance your oral formulations with high quality ingredients. Contact us to learn about the excipients in development.

-
Product CARBOWAX™ SENTRY™ Polyethylene Glycol (PEG)
CARBOWAX™ SENTRY™ PEGs common applications include: carrier/plasticizer in gel capsules, base for face/neck lotions, providing formulation stability in toothpaste, binder for tablets, shampoo wetting agent, and more. CARBOWAX™ SENTRY™ PEGs are available in average molecular weights ranging from 3...
-
Product MANNITAB™ SD1
Mannitol powder
Binder for direct compression
USP/NF, Ph. Eur., BP, IP
Particle size: 100 µ

-
Product Tacrolimus capsule
Hangzhou Zhongmei Huadong Pharmaceutical provides wide range of pharmaceutical products which includes tacrolimus capsule. It belongs to formulation category. Indication: for prevention of transplant allograft rejection after liver or renal transplantation. For treatment of transplant allograft rejection f...
-
Product We take your products from idea to market success
Hänseler Swiss Pharma is a dedicated partner known for its unwavering commitment to the highest quality standards and innovative strategies. We bring our enthusiasm and Swiss precision to support our partners across the entire value chain, providing custom-tailored solutions for your success in the pha...
-
Product Lactalpha 50
Lactalpha 50 is a 50 Mesh pharmaceutical grade sieved lactose conforming with the lactose monohydrate monograph of the current Pharmacopoeias (Ph. Eur., USP-NF and JP). The flowability of Lactalpha 50 makes it efficient as a diluent in capsule or sachet formulation.
Manufactured in Retiers,...
-
Product Scientific Support
Selectchemie AG provides a wide range of services including scientific support. Our experienced professionals are at your service at locations in 18 countries to deliver tailor-made solutions according to your needs. Contact us for more information.
-
Product Montanox™
The MONTANOX™ range is composed of different grades of polysorbates that can be used to solubilize active pharmaceutical and/or biological ingredients and to formulate oil-in-water emulsions for oral, topical and injectable products.
• MONTANOX™20 PHA PREMIUM: Polysorbate 20 • MONTANOX™60 PHA PREMIU...
-
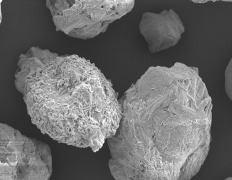
Product Recombinant Human Hyaluronidase
Hyaluronidase, an enzyme that breaks down hyaluronic acid, has long been used to facilitate the dispersion and absorption of other drugs and to reduce tissue damage in cases of extravasation of a drug. Recombinant human hyaluronidase (rhPH20) developed by BaoPharma (Shangh...
-
Product Benecel™ HPMC DC
benecel™ hypromellose (hydroxypropyl-methylcellulose or HPMC) is a versatile excipient with a variety of applications. HPMC is the most widely used polymer in hydrophilic matrix systems with widespread use in controlled-release dosage forms.
benecel™ DC HPMC is a surface modified, co-proce...
-
Product SANAL® P+ Pharmaceutical Sodium Chloride (API)
SANAL® P+ Sodium Chloride Pharmaceutical Quality is for specific market requirements (eg. the Chinese and Russian markets) as active ingredient in both parenteral and peritoneal solutions and a base material for hemodialysis and hemofiltration solutions as well as other pharmaceutical applic...
-
Product Low-substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose/LHPC
Anhui Sunhere Pharmaceutical Excipients offers wide range of pharmaceutical products which includes maize starch/corn starch. Packaging: 25kg/kraft bag; 25kg/fiber drum. Main purpose: tablet and capsule diluent;tablet and capsule disintegrant;. Contact us for more information.
-
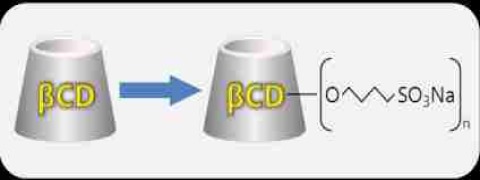
Product Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium
Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium is a new type of anionic high soluble cyclodextrin derivatives. It could include drug molecules to from covalent compounds so that increase the drug’s stability,solubility,safety.It could reduce the renal toxicity,moderate drug’s hemolysis,control the release rate and cover ...
-
Product LACTOSE (80M, 200M, ANHYDROUS)
PHARMALACT® 200M is finely milled α-lactose monohydrate powder meticulously manufactured by Pfeisinger GmbH. This product, defined by its 200-mesh particle size, redefines excellence in tablet manufacturing through optimal compaction and blending properties.PHARMALACT® 80M, a coarse free-flow...
-
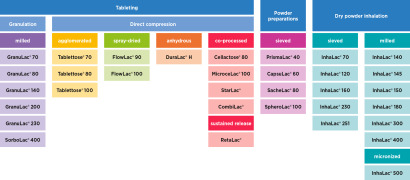
Product Lactose Product Portfolio
MEGGLE has it: The Right Lactose Product for all Needs
The world of lactose is our whole world. With this in mind, our products are aligned specifically to your needs and applications. For further information on any product shown here, please see the detailed, individual product brochure ava...
-
Product BC SIMETHICONE ANTIFOAMS FOR PHARMACEUTICAL APPLICATIONS
Momentive offers a range of pharmaceutical-grade silicone antifoams (Simethicone) in compliance with US and European Pharmacopeia standards. Our solutions are versatile and deliver value to stakeholders across the pharmaceutical value chain, such as pharmaceutical ingredient manufacturers, finished do...
-
Product SuperTab® 30GR
SuperTab® 30GR is a highly consistent, agglomerated monohydrate lactose processed utilising a unique production technology. The granule structure (containing small primary particle sizes), as a result of fluid bed processing, provides optimal flow / compaction ratio allowing easy direct compression pr...
-
Product Primary Pharmaceutical Reference Standards and Reference Material Management Services
Discover our extensive range of high-quality pharmaceutical reference standards:
- Over 6,000 APIs, excipients and impurities for qualitative and quantitative applications
- Many APIs & excipients ISO 17034 accredited
- 95% ready to ship
- Comprehensive CoA...
-
Product Dispersome® Technology
Dispersome®️ – A green technology for drugs
The Dispersome® technology uses high quality whey protein, an environmentally friendly by-product from cheese production, to improve the solubility and bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs.
To watch explanatory Dispersome...
-
Product Dimethyl Sulfoxide (USP, BP, Ph. Eur.) pharma grade CODE 191954
https://www.itwreagents.com/iberia/en/product/dimethyl-sulfoxide-usp-bp-ph-eur-pharma-grade/191954
-
Product Ferrous Bisglycinate
Dr. Paul Lohmann GmbH & Co. KGaA offers a wide range of Iron products. Please contact us for more Information. -
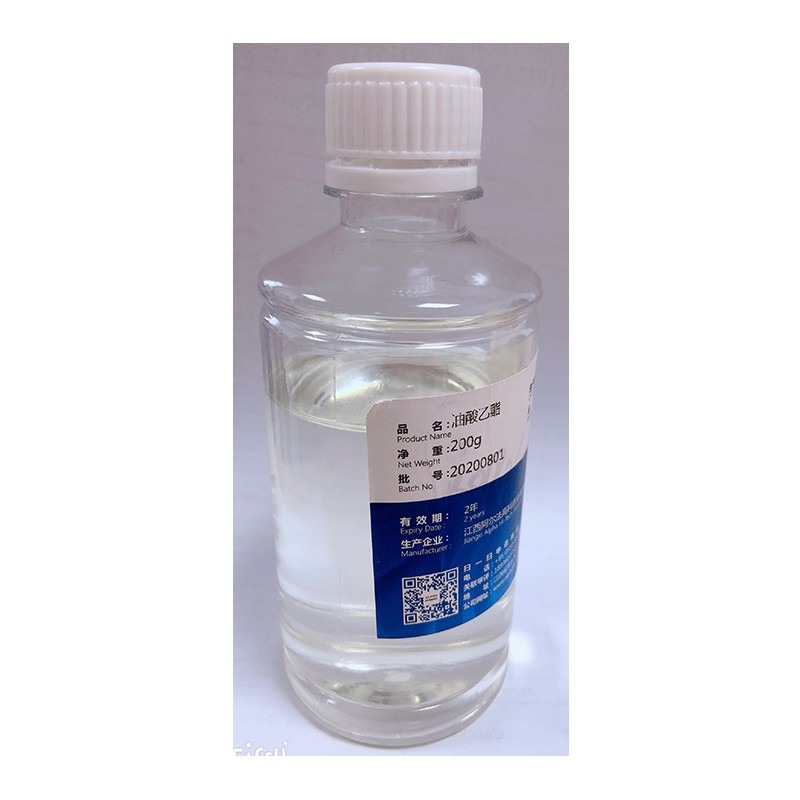
Product Ethyl Oleate
Appearance: Colorless to pale yellow clear liquid.
Almost insoluble in water, miscible with ethanol, dichloride methane or petroleum ether. It can be miscible with isopropanol in any proportion. Application:
Used as a solvent, a transdermal absorption enhancer, a lubricant and a pl...
-
Product Macrogol 400 / Hedjuvan-MG400
Hedjuvan-MG400 is a high quality Macrogol 400. The product is produced at Kolb in Hedingen (Switzerland) and is getting tested according to the specifications of the current Ph. Eur. and USP. Kolb has a broad portfolio of non-ionic surfactants with polysorbates having a long successfull trac...
-
Product Sodium Hyaluronate - Injection grade
Hyature® is a pharmaceutical grade sodium hyaluronate which can be used as an API or excipient for drugs and medical devices in ophthalmic preparations, intra-articular injections, anti-adhesive preparations, topical preparations for wound healing and soft tissue filler, etc. Hyature® sodium hyalur...
-
Product Polygeline
Serumwerk Bernburg AG is a knowledge base regarding the production of polymer-containing sterile solutions, which can be used for a wide variety of purposes (e.g. volume replacement therapy, adjuvant in the production of vaccines). In recent years, customized formulations based on starch or gelatin have be...
-
Product Neohesperidin Dc pharma grade
Our Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone serves as an excipient, fulfilling a dual role as both a sweetener and a masking agent in oral drug delivery formulations. This additive is obtained through the hydrogenation of Neohesperidin, a flavanone naturally occurring in bitter oranges (Citrus aurantium). Its primar...
-
Product Calcium Carbonate IP BP USP EP JP Oyster Coral
We are considered in the market to be one of the leading manufacturers and suppliers of this commendable Calcium Carbonate IP BP USP EP JP and OYSTER. Processing of this product is done in accordance with the set norms and guidelines of the chemical industry, utilizing the finest ingredients and ...
-
Product Multifunctional Excipients for the Nutraceutical and Pharmaceutical Industry
Our SYLOID® FP silica excipients are a strategic drug development tools in today’s challenging pharmaceutical industry with its demands for improved formulations, bringing new drugs to market faster, and technological advances.
SYLOID® FP silica’s unique, innovative design combine...
-
Product Contract R&D and Scale-Up
Actylis offers GMP, biopharma and non-GMP specialty chemical custom ingredient research and development services by generating robust, practical and cost-effective processes for the preparation of specialty chemicals, excipients, and pharmaceutical ingredients. With decades of experienc...
-
Product AnyCoat-C® (Hypromellose); HPMC; Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose
AnyCoat-C® is a beloved brand name of the cellulose ether manufactured by LOTTE Fine Chemical.
Properties: white or yellowish white powder; soluble in mixed organic or aqueous solvent; making up transparent film when solvent remove.
Applications: Pharmaceutical excipient, food...
-
Product Trusted Ingredients for Pharmaceuticals
With Spectrum Chemical, meet the requirements specified in the USP and NF monographs, which are the official standards for all prescription and over-the-counter medicines, dietary supplements, excipients and other healthcare products.
- Ideal for parenteral, oral, topical and ophthal...
-
Product Copovidone VA64/ PVP VA64
Copovidone is a water-soluble polymer resin, white powder, odorless and tasteless, easy to absorb moisture, soluble in water, ethanol and anhydrous alcohols, with good cohesiveness, hygroscopicity, film-forming properties and surface activity.The main application is as follows,
(1)Pharmaceutical field: ...
-
Product Sodium Dextran Sulfate 5000
Sodium Dextran Sulfate 5000 suitable for pharmaceutical field with high quality.
-
Product Sunvidone ®K/Povidone K series
Huzhou sunflower pharmacetuical co. Ltd offers a wide range of products which includes povidone K series. Feature: it is an aqueous solution of synthetic polymer compound is n vinyl pyrrolidone polymers are linear. It is white to milky white amorphous powder, having a bulk density of 0.4 to 0.6; odor...
-
Product Armor Pharma Lactose Monohydrate 80M
Latest launch: ARMOR PHARMA™ lactose monohydrate 80M is a coarse free flowing powder of α-lactose monohydrate with typical Tomahawk shape.
Sieving process gives coarse particles with a narrow particle size distribution enabling very good flowability. This lactose is very often used in capsules a...
-
Product Polyglykol
Effective and high-purity ingredients including a complete range of Polyglykols (Macrogols) our universally applicable pharmaceutical polymers, with various molecular weights, supported by CEP certification and DMF type II documentation.
-
Product Expansorb
Poly(lactic acid co-glycolic acid) and poly(caprolactone) copolymers used as functional excipients for controlled and slow drug release (weeks to months) with a single injection.
-
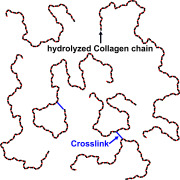
Product CROSCARMELLOSE SODIUM
odium croscarmellose is an internally cross-linked sodium carboxymethylcellulose for use as a superdisintegrant in pharmaceutical formulations.
-
Product LIGAMED MF-2-V-MB
LIGAMED MF-2-V-MB is our most widely used excipient for the production of tablets and capsules. Its high specific surface area and fine particles offer a high releasing speed during tablet pressing and consistent physical performance of the tablets such as hardness and dissolution profiles. Due to the exce...
-
Product Excipient: Super Refined™ DEGEE
Super Refined DEGEE is ideal for use in topical and transdermal applications to enhance the permeation of poorly water-soluble API’s through various layers of the skin, thereby improving drug delivery. It can also be used as a co-solvent in self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS), or self-microe...
-
Product PHARCOCEL - HPMC / Hypromellose / Hydroxy Propyl Methyl Cellulose
Pharmaceutical grades of HPMC will have detailed specification as per specific monograph. All our HPMC grades will be available in powder & granular form.
-
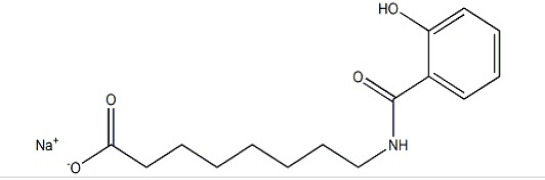
Product SNAC CAS 203787-91-1
CAS:203787-91-1
Molecular Weight:301.31337
Molecular Formula: C15H20NNaO4
Appearance: white powder
Application: medical intermediate
Delivery Time: Available goods in stock
Package: inside: douple PE bag outside: paper drum
...
-
Product APISAL (Sodium chloride API)
For the exceptionally high requirements in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes, we produce pure pharmaceutical salt exceeding the purity requirements stipulated in the pharmacopoeias. All steps of production, analysis, and quality control comply with these strict principles. APISAL® is obtained from a p...
-
Product DRCOAT - Customised Ready to use Coating Pharma Polymer
ENTERIC COATING (AQUEOUS / NON AQUEOUS)IMMIDIATE RELEASE FILM COATING / FILM COATING
MOISTUER BARRIER COATING
PEARSCENT COATING / METTALIC COATING
GLOW COATING / GLOSS COATING
TRANSPARENT COATING

-
Product PharmaSugar®
PharmaSugar® is the benchmark for formulations requiring dry or liquid sugar as an excipient.
Our products are manufactured by ISO 9001, ISO 14001, FSSC 22000 certified, GMO-free and ANSM registered sugar refineries. The batch-based management of PharmaSugar® products ensures full tr...
-
Product PEARLITOL® - Mannitol
PEARLITOL® Mannitol pharma range is used as a filler and filler/binder as well as a bulk sweetener. The PEARLITOL® range offers a unique blend of exceptional physical and chemical stability and no hygroscopicity.PEARLITOL® can be used in various oral dosage forms in both pharmaceutical and nutraceutic...
-
Product Stearic Acid
Stellipress Brand ensures EP/USP compliance of our high purity Micronized Stearic Acid.
Our Stearic Acid is your best choice as a Tablet Lubricant and Magnesium Stearate replacement.

-
Product Embo caps®
Suheung capsules offers a wide range of products which includes embo caps. It belongs to empty hard capsules category.
By embossing four dimples on the main locking groove of the cap, the exclusive EMBO CAPS® is designed to offer distinct advantages.
To eliminate premature semi-locking and final...
-
Product Taste masking Agent for Ciprofloxazin (Doshion P 544 DS CIPRO - Potassium Salt of Weak Acid Cation Resin)
Application- • Taste masking of Ciprofloxazin HCl for suspension and dry syrup
-
Product Emulfree Duo
Emulfree® Duo is a ready-to-use system. It has been designed to stabilize the oil phase within a bi-gel, an emerging topical formulation, by ensuring fine and homogeneous dispersion in the aqueous phase. As a PEG-free excipient, it is ideal for sensitive skins and mucosea.

-
Product EUDRAGIT® Functional Polymers
Evonik is a global development partner and solutions provider for oral drug delivery. For more than 60 years, we have been providing renowned pharmaceutical and biotech companies with oral drug delivery solutions to help them enhance drug performance, reduce project complexity, increase speed to market and...
-
Product SÜDZUCKER COMPRI® M3000
Südzucker COMPRI® M3000 is an agglomerated, directly compressible sugar with parts of maltodextrin. It is suitable e.g. for the production of confectionery or pharmaceutical tablets.
PRODUCT BENEFITS
· Di...
-
Product Excipia Experts in excipient analysis, characterization and deformulation / reverse engineering
Excipients can have an important impact on the manufacturability and pharmaceutical performance of a formulation. It’s therefore important to identify and control functionality related characteristics (FRCs) of excipient materials in order to achieve safe, robust and stable products. Expe...
-
Product Manufacturing
Custom API Manufacturing, Fermentation, Finished Dosage Form, High Potency, Lipid Nanoparticle, Rare / Orphan, Stability & Release Testing, Sterile Fill Finish, APIs & Intermediates, Fine Chemicals

-
Product Hydroxypropylcellulose low-substitued (L-HPC)
Your benefits
- wide range of types to cover various applications and technologies
- produced according to IPEC-GMP guidelines
- Chinese DMF available
- increase the stability of your API in the finished dosage form and enables formulation of smaller table...
-
Product TABLUBE - MAGNESIUM STEARATE
Nitika Pharmaceutical Specialities Pvt Ltd provides wide range of excipients which includes Tablube - Magnesium Stearate. It's a type of lubricants and glidants.
Product Description:
· DMF Available
· &nbs...
-
Product galenIQ™ 720
BENEO-Palatinit GmbH provides the pharmaceutical excipient galenIQ™ 720. It is an agglomerated spherical isomalt for direct compression and powder applications. General benefits: high agglomerate stability and excellent flow; morphology ensures homogeneity of the mix and content uniformity; very low compre...
-
Product POVIDONE, MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE, HYPROMELLOSE, CROSPOVIDONE, COPOVIDONE, CCS, COLLOIDAL MCC, LACTOSE, STARCH, SUCRALOSE, SACCHARIN, CYCLODEXTRINS, POLOXAMER, POLYSORBATE, PEG, API, INTERMEDIATES, FILTER BAGS, SILICA, SILICONES,
DILUENTS, BINDERS, DISINTEGRANTS, FILM FORMERS, PLASTICIZER, POLYMERS, SWEETENERS, SURFACTANTS, PEPTIDES, OMEGA 3 FATTY ACID, VITAMINS, DIETARY FIBRES, COCOA POWDER, ANTI AGEING, ANTI WRINKLES, MOISTURIZERS, ENCAPSULATED BEADS, SCRUBING BEADS,
-
Product TRIS
English Name:Tromethamine
Molecular Formula:C4H11NO3
Molecular Wt:121.14
CAS:77-86-1
Assay : ≥99.5%
Appearance : White crystalline powder
TRIS is an important pharmaceutical intermediate that can be used to synthesize dexketoprofen tromethamine and ...
-
Product Dexolve
Dexolve is the first generic USP and EP-conform Betadex Sulfobutyl Ether Sodium for:• solubility enhancement (10 to 100,000 fold) • Improvement of chemical stability • Increased bioavailability, facilitated delivery • Reduced aggregation • Moderate irritationor reduced side-effects • Maximiz...
-
Product BENTONITE IP | BP | NF
Bentonite is used as filler in pharmaceuticals and due to its absorption functions it allows paste formation. Bentonite is used as an antidote in heavy metal poisoning.
Used in personal care products animal feed industry mud packs sunburn creams
-
Product MICCEL-101 (Microcrystalline Cellulose)
Ankit Pulps & Boards Pvt Ltd offers a wide range of products which includes MICCEL 101.
Feature: Wet Granulation and Direct Compressible.
LOD %: NMT 6.0/7.0;
BD g/ml: 0.22 to 0.34;
+60 #, %: NMT 1
+200 #, %: NMT 30
Contact us for more information at&nb...
-
Product Compritol® 888 ATO
A glyceride with a high melting point used as a modified release agent or lubricant in tablets. Can also be used in lipid coating technologies and as lipid carrier for nanoparticles. UNII Code (FDA): R8WTH25YS2
Preferred Substance Name (FDA): GLYCERYL DIBEHENATE
Handbook of Pharmac...
-
Product SORBITOL 70% SOLUTION
Sorbitol 70% (D-Glucitol) SolutionGulshan Polyols, is one of the largest manufacturers of Sorbitol (D-Glucitol) with a capacity of 72000 MTPA in India. GPL's Sorbitol 70% (D-Glucitol) solution facility is an ISO 9001:2008, HACCP, OU-Kosher, HALAL & FSSAI certified company. It also meets&...
-
Product Organic & Inorganic Bromide
Organic & Inorganic Bromide like Ammonium Bromide, Hydrobromic Acid 48%, Lead (II) Bromide Anhydrous, Manganese (II) Bromide Tetrahydrate, Nickel (II) Bromide Anhydrous, Potassium Bromide, Strontium Bromide Anhydrous, Strontium Bromide Hexahydrate, Magnesium Bromide Hexahydrate, Antimony (III) Bromide,...
-
Product Topical Excipients
Biesterfeld Spezialchemie GmbH offers a wide range of pharmaceutical excipients for topical formulations in various forms. For example silicone fluids & volatiles, cyclics, silicone blends, zinc oxide, glycerin, carmellose sodium, stearates, parabens etc.
-
Product DiCOM - DC
DiCOM - DC - For small dose API and large dose API with good compressibility DiCOM - DC PL - For small dose API and large dose API with good compressibility
DiCOM - DC DT - For low disintegration time formulations
DiCOM - DC SP - For li...
-
Product Excipient grade
Pharma Excipients:
The globalisation of the pharmaceutical industry combined with a global regulatory has created a need for a comprehensive excipient quality and control standard. Our FDA approved manufacturing facility with IOS 9001:2015 to produce high quality pharmaceutical excipients...
-
Product J.T.Baker® Viral Inactivation Solution
J.T.Baker® Viral Inactivation Solution Biotech Reagent is a highly effective, ready-to-use product, specifically developed for detergent-based viral inactivation in biopharmaceutical operations and plasma derived therapy processes. J.T.Baker® Viral Inactivation Solution is formulated with non-ionic deterge...
-
Product OMYAPHARM 500-OG
OMYAPHARM 500-OG is a multifunctional mineral excipient. It is functionalized Calcium carbonate.
-
Product Ascorbic Acid(Vitamin C)
(5R)-5-[(1S)-1,2-Dihydroxyethyl]-3,4-dihydroxyfuran-2(5H)-one.white or almost white, crystalline powder orcolourless crystals, becoming discoloured on exposure to airand moisture. Freely soluble in water, sparingly soluble in ethanol(96 per cent).
-
Product Aduxol OP-010/ E
Octoxinol 10 is used as a detergent in biochemistry. Not
denaturizing proteins, it is used in protein purification to
solubilize membrane proteins in their native conformation
from membranes. It is also used for viral inactivation
of enveloped viruses by the solvent detergent method. qq...
-
Product CROSPOVIDONE TYPE A & CROSPOVIDONE TYPE B
Crospovidone is a white to creamy-white, finely divided, free flowing, practically tasteless, odourless or nearly odorless, hygroscopic powder.
-
Product Fumed Silica
Product description.
EMRASIL200 is a medium surface Fumed Silica, Synthetic,hydrophilic, amorphous silica,also named as Colloidal SiliconDioxide. Produced via flame hydrolysis.
Special features
White colloidal powder of high purity.
Tasteless, colorless, odorless;...
-
Product Magnesium Oxide
Magnesium oxide (MgO) is a white solid at room temperature and exists in nature as periclase. It can be produced by calcining basic magnesium carbonate or magnesium hydroxide, or using carbon dioxide as an oxidant. Magnesium oxide is slightly soluble in water and soluble in acid. It has a wide range of app...
-
Product Liquid Flavours
Liquid flavours for formulation ranging from sweet orange to bittermask flavours.
-
Product Sheffield Pharmaceutical Grade Lactose
Kerry has over 85 years experience as a leading global manufacturer of excipients. We manufacture an extensive line of anhydrous, spray dried and monohydrate grades of lactose meeting NF/JP/EP monographs in a variety of particle sizes
-
Product Microcrystalline cellulose CEOLUS™ KG
CEOLUS™ KG Grades is highly compactible MCC with fibrous particles. Enable poorly compactible and/or high dose formulations. Solve tableting issue such as insufficient hardness, sticking or capping. Also enable unique and patient friendly dosage form like MUPS, ODT, multiple-layers, multiple APIs combinati...
-
Product ASHACEL ETHYLCELLULOSE
ASHACEL ETHYLCELLULOSE EXCIPIENT USED FOR CONTROLLED RELEASE, MOISTURE BARRIER AND TASTE MASKING PURPOSES IN PHARMACEUTICALS. ASHA ALSO OFFERS TECHNICAL SUPPORT TO ITS CLIENTS WHEN IT COMES TO USE OF ITS PRODUCTS IN THEIR FORMULATIONS.
-
Product CALCIUM CARBONATE POWDER
CALCIUM CARBONATE IS BEING USED FOR CALCIUM SUPPLIMENTION IN PHARMA AND FOOD INDUSTRY.
-
Product UNIGEL 270
UNIGEL 270 IS A PHARMA GRADE PRE-GELATINIZED STARCH PRODUCED FROM CORN UNDER SPECIFIC PROCESS AND CONDITIONS AND PARAMETERS WHICH COMPLY GMP AND FDA PRODUCT STANDARDS.
-
Product Excipients
Patel Chem Specialities P. Ltd. is leading manufacturer of Pharmaceutical excipietns like....
(1) Rheollose® - Sodium Carboxy Methyl Cellulose IP, BP, EP, USP-NF (Sodium CMC)(US DMF No. 033401)
(2) BlowTab® - Sodium Starch Glycolate (Type-A) (Mai...
-
Product Trehalose SG
Trehalose is a dihydrous and non-reducing disaccharide consisting of two glucose molecules linked by an a, a-1, 1 bond. Our TREHALOSE SG is monographed as being low endotoxin and intended mainly for injection. Its remarkable stability makes this sugar an ideal excipient as a stabilizer ...
-
Product Chenodeoxycholic Acid Sodium Salt
ICE S.p.A provides a wide range of products which includes chenodeoxycholic acid sodium salt. It has been the same pharmacological properties of chenodeoxycholic acid. It reduces cholesterol amount, probably by inhibiting liver synthesis, allowing gallstones dissolution. Packaging: lab or pilot scale scale...
-
Product Acetic Acid, Glacial (99.9%)Ph.Eur./USP/JP parenteral grade
Aug. Hedinger GmbH & Co. KG offers a wide range of products which includes acetic acid, glacial (99.9%)parenteral grade from the producer Wacker. Contact us for more information.
Available sample CofA, Specification, MSDS, Productflyer etc.

-
Product Acrycoat® Methacrylic Acid Copolymer
Acrycoat® family of polymers are Methacrylic acid copolymers type A, B & C which confirms to USP/NF, EP and JP specification.
Immediate Release: The Immediate release series work in wide application range which includes tablet binding, taste masking, odor masking and provi...
-
Product HiCel™ SMCC - Overspeed on your Tablet Press
HiCel™ SMCC is an innovative combination of MicrocrystallineCellulose Ph.Eur., USP-NF,JP, and Colloidal Silicon Dioxide Ph.Eur., USP-NF, JP by co-processed technology. This Co-processing technology leads to the formation of co-processed excipient with superior physical properties compared to simple physica...
-
Product Active pharmaceutical ingredients
Imcd india pvt. Ltd. provides a wide range of active ingredients products which includes active pharmaceutical ingredients. It is a comprehensive dedicated sourcing service with locations in mumbai and shanghai coupled to a europe-based project coordination and project management service. Contact us for mo...
-
Product Aceclofenac
Generex Pharmassist Pvt. Ltd provides wide range of formulations which includes aceclofenac. Therapeutics: anti pyretic, anti arthritic & nsaids. Dosage form: tablets, syrups. Contact us for more information.
-
Product (1) PROTECTAB HP-1 , (2)PROTECTAB MB-1, (3) PROTECTAB ENTERIC M-1, (4)PROTECTAB HP-2, (5) PROTECTAB HP-2 TRANSPARENT, (6) PROTECTAB HP-2 PEARL FINISH, (7)PROTECTAB EC-1, (8)PROTECTAB OM-1, (9) HYPRO SR-1 (10) ENHANCE DT
1. PROTECTAB HP1 (HPMC based, Organic/Aqueous Film Coating Material) 2. PROTECTAB MB-1 (Moisture Barrier Film coating material)
3. PROTECTAB ENTERIC M1 (Methacrylic Acid Copolymer based Enteric Coating material),
4.PROTECTAB HP-2(High Film strength HPMC based Film Coating Material),
5. PROTEC...
-
Product Calcium Carbonate IP/BP/USP
Calcium Carbonate is a calcium salt with formula CCaO3. it has a role as an antacid, a food colouring, a food firming agent and a fertilizer. it is a calcium salt, a carbonate salt and a one carbone compound.
-
Product WINCOAT WT-MPAQ Moisture Protective Aqueous film coating
Wincoat Colours & Coatings Pvt.Ltd. offers wide range of functional film coating products which includes wincoat wt – mp – moisture protective film coating. It is recommended for hygroscopic products which are sensitive to moisture. It is one step coating system gives high level of moisture protection ...
-
Product YTZ Grinding media
Grinding Media for wet milling process , compatible with pharmaceutical applications for API particle size reduction to nano scale. YTZ® is recognized by users as the best available product for grinding process, providing highest quality results for employed processes. Complete traceability from... -
Product Calcium Carbonate
CFL-Chemische Fabrik Lehrte GmbH provides wide range of products which includes calcium carbonate light and heavy. Contact us for more information.
-
Product Excipients
Carbomers, Castor Oil Derivates, Acrylate Copolymer, Calcium Carbonate, Carboxymethylcelullose, Crosspovidone, Calcium Phosphate, Ethylcellulose, Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose HPMC, Lactose Monohydrate, Magnesium Stearate, Maltose, Microcrystalline...
-
Product Liquid Paraffin
Synonyms: White Mineral Oil, Liquid Vaseline, Paraffin Oil, White Oil
Grades, CX, PX and LX (Light and Heavy)
INTRODUCTION:
· Our entire range of Mineral Oil are purified mixture o...
-
Product Hydroxypropylcellulose
IMCD N.V. Offers a wide range of excipients which includes hydroxypropylcellulose. Contact us for more information.
-
Product Acrylic Acid Polymer
Arihant Innochem Pvt Ltd offers a wide range of Pharmaceutical Excipients which includes Acrylic acid polymer. Contact us for more information.
-
Product Glycine
This amico acid can be used as a starting material, feed additive, food additive, cosmetical ingredient, excipient or API.

-
Product Excipient
Dksh india pvt. Ltd offers a wide range of ingredients which includes excipient. Contact us for more information.
-
Product Aspirin Pellets 60%
Cornileus pharmaceuticals (p) ltd offers a wide range of products which includes aspirin pellets 60%. It belongs to pellets category. Contact us for more information.
-
Product (1R,2R)-1,2-Cyclohexanedimethanol
Yasham speciality ingredients private limited provide a wide range of excipients products which includes (1r,2r)-1,2-cyclohexanedimethanol. Contact us for more information.
-
Product Bleomycine Sulfate
NORTHEAST PHARMACEUTICAL GROUP CO.,LTD. provides wide range of products which includes bleomycine sulfate. It belongs to anti cancer series category. Contact us for more information.
-
Product Heparin Sodium
Hubei Enoray Biopharmaceutical Co Ltd provides wide range of products which includes heparin sodium. Contact us for more information.
-
Product 5 - fluorouracil injection usp
Flagship Biotech International Pvt. Ltd offers wide range of oncology products which includes 5 - fluorouracil injection usp. Contact us for more information.
-
Product Calpol
Ethypharm offers pharmaceutical products which includes calpol. Contact us for more information.
-
Product 5'-Deoxy-Fluorouridine(Doxifluridine)
Zhejiang Guobang Pharmaceutical Co Ltd offers a wide range of products which includes 5'-Deoxy-Fluorouridine(Doxifluridine). Contact us for more information.
-
Product Amlodipine besylate Film-coated tablet
HEC Pharm Group provides wide range of products which includes amlodipine besylate film-coated tablet. It belongs to formulation category. Contact us for more information.
-
Product (Qing Chi Ling) lecithin tablets
Gansu dadeli pharmaceutical co., ltd offers a wide range of products which includes (Qing Chi Ling) lecithin tablets. It belongs to prescription drugs - non-antibiotic - Tablets category. It is is extracted from natural egg yolk, so far not found any reports of adverse reactions and side effects.. Package:...
-
Product 4% TMP+40% Sulfadiazine
Hebei veyong animal pharmaceutical co. offers a wide range of products which includes 4% TMP+40% Sulfadiazine. It belongs to solution for oral category. Content: 100ml, 250ml.500ml, 1000ml. Diversified specification and package are available on the basis of clients needs. Contact us for more information.
-
Product Excepients
Vitalchemie provides a wide range of pharmaceutical products and services which includes excepients. Contact us for more information.
-
Product Espheres CACO3
Ideal cures has a wide range of products which includes espheres CACO3.It consist of CaCO3 and also used for the controlled release and MUPS formulations in nutraceutical and pharmaceutical medicine.It contains not more than 90% of calcium carbonate, calculated on the dried basis. It is adapted for control...
-
Product 2-FDC HR 150/300
Chongqing Huapont Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd provides wide range of formulations which includes 2-fdc hr 150/300. Packaging: 15 pills×4 plates. Contact us for more information.
-
Product Salicat cpm
Salicylates & Chemicals Pvt. Ltd offers wide range of pharmaceutical products which includes salicat cpm. INCI: chlorphenesin, methyl paraben, propylene glycol. Contact us for more information.
-
Product Allantion
Scope Ingredients Pvt. Ltd offers wide range of excipients which includes allantion. Application: emollients. Contact us for more information.
-
Product Vitamin d2 crystal
Taizhou hisound pharmaceutical offers a wide range of products which includes vitamin d2 crystal. It belongs to Pharmaceutical Drugs category. It also known as ergocalciferol, has the physiological function to promote intestinal calcium absorption, regulate calcium and phosphorus metabolism and induce bone...
-
Product Acebrofylline
Theon Pharmaceuticals Ltd. offers wide range of pharmaceutical products which includes acebrofylline. Contact us for more information.
-
Product Ammonium Di Hydrogen Phosphate
CAS NO:7722-76-1HSN CODE:28352990
MOLECULAR FORMULA:NH4H2PO4
MOLECULAR WEIGHT:115.03 g/mol
FORM:Powder
APPEARANCE/DESCRIPTION:Colorless or white crystals or crystalline powder ASSAY:98.0 % - 101.0 %
PACKING SIZE:25 Kg Bag
-
Product MANNITOL
We are sole selling agents of Qingdao Brightmoon Mannitol in India. Product is compliant with Halal, Kosher and Vegan norms. It is used as a excipient and as API. It is free from GMO, Melamine, Aflatoxins, Allergens, Gelatin, Gluten, BSE-TSE and other contaminants.
-
Product TARTARIC ACID PALLETS ,USP-NF PH.EUR (ALL MESH SIZE)
For your info we would like to inform you that our principal IPS Srl has received pre-assigned DMF for IPS Srl TARTARIC ACID PELLETS.
Also Once product commercialize scale,we agree in receiving a visit to our principal manufacturing plant for our customers.

-
Product Excipients
Solubilizer, Lubricant, Buffering Agent, Filler, Antacids, Sweetener, Emollient, Alkalinizer, Base, Viscosity Modifier, Humectant, Diluents, Processing Aid and Buffer
-
Product 1,2 Propylene glycol
For more information please contact us at [email protected] or call us at 022-62431515
-
Product HPMC
Hypromellose or HPMC solutions were patented as a semisynthetic substitute for tear-film.[8] Its molecular structure is predicated upon a base celluloid compound that is highly water-soluble. Post-application, celluloid attributes of good water solubility reportedly aid in visual clarity. When applied, a h...
-
Product Cross Povidone XL -10 USP
Iris ingredients provides a wide range of products which includes cross povidone xl -10 usp. Application: it is a common inactive ingredient used in the pharmaceutical industry. Chemically crospovidone is an inert and insoluble white to light yellow free-flowing powder, it has hygroscopic or water-attracti...
-
Product Syloid fp
Singhania & sons pvt ltd offers a wide range of products which includes syloid fp. It belongs to excipients category. Contact us fore more information.
-
Product Arginine
Shenzhen China Resources Gosun manufactures & market cephalosporin products which includes Arginine. It belongs to formulation products category. Contact us for more information.
-
Product Excipients
Citric Acid AnhydrousTrisodium Citrate Anhydrous
Trisodium Citrate Dihydrate
Glucono-delta-Lactone
Sodium Gluconate
Calcium Lactate Gluconate
Monosodium Citrate
Potassium Gluconate
Tricalcium Citrate
Trimagnesium Citrate
Tripotassium Citrate
Zinc Citrate
CITROFOL® AI C...
-
Product ETHOCELâ„¢ Premium Ethylcellulose Resins
An excellent choice for modified release
ETHOCELâ„¢ premium ethylcellulose resins are water-insoluble polymers. They are soluble in a wide range of organic solvents, beginning with aliphatic alcohols such as ethanol and isopropanol, and are compatible with most other familiar organic solvent chemi...
-
Product METHOCELâ„¢ Cellulose Ethers
Well-recognized product that can do it allMETHOCELâ„¢ cellulose ethers are water-soluble polymers derived from cellulose. The METHOCELâ„¢ product range encompasses methylcellulose and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (hypromellose) “ each available in different grades to address a wide range of applications i...
-
Product Edetate Disodium USP (VERSENE™ NA)
VERSENE™NA Chelating Agent is an effective stabilizer and preservative for pharmaceutical preparations, including medicated creams and ointments, ocular care, syrups and elixirs. This Edetate Disodium USP-grade product controls metal ions present in pharmaceutical formulations or processes. Product B...
-
Product UNI-PURE® WG 220
Fully Pregel Starch, Corn
Binder for Direct Compression
USP/NF, Ph. Eur.,Ch.P
-
Product UNI-PURE® F
Native Starch, Corn
Extra-White Filler
USP/NF, Ph. Eur., JPE
NMT: 15% Moisture
*NMT: Not more than
-
Product UNI-PURE® FL
Native Starch, Corn
Low Moisture Filler
USP/NF, Ph. Eur. , JPE
NMT: 2% Moisture
*NMT: Not more than
-
Product MANNITAB™ SD2
Mannitol powder
Binder for direct compression
USP/NF, Ph. Eur., BP, IP
Particle size: 200 µ

-
Product Liquid Solutions
Chemical solutions (GMP-compliant): • API & excipients • Hazardous materials • Explosives • Filling under inert gas
Special extracts and tinctures: • Mother tinctures • Boswellia extract • Opium tincture • Capsicum extract • Henbane extract • Cannabis extract
Packaging • 2...
-
Product Semi-Solid Solutions
We produce ointments, creams, emulsions, pastes, and gels (including basic components) through our systems. This encompasses both semi-finished and final products, including pharmaceuticals. The manufacturing process, whether automated or semi-automated, depends on the order volume. Hänseler Swiss Phar...
-
Product Solid Solutions
We specialize in the manufacturing of bulk powder mixtures in compliance with GMP standards, offered as premixtures, active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), or finished pharmaceutical products.
Manufacturing
Powder mixtures (premixtures o...
-
Product Lactalpha 100
Lactalpha 100 is a 100 Mesh pharmaceutical grade milled lactose conforming with the lactose monohydrate monograph of the current Pharmacopoeias (Ph. Eur., USP-NF and JP). The flowability of Lactalpha 100 makes it efficient as a diluent in capsule or sachet formulation.
Manufactured in Retie...
-
Product Lactalpha 150
Lactalpha 150 is a 150 Mesh pharmaceutical grade milled lactose conforming with the lactose monohydrate monograph of the current Pharmacopoeias (Ph. Eur., USP-NF and JP). Lactalpha 150’s fine mesh enables it to be used as a binder or diluent for tableting after dry or wet granulation, along with guara...
-
Product Commercial Support
Selectchemie AG provides a wide range of services including commercial support. Our experienced professionals are at your service at locations in 18 countries to deliver tailor-made solutions according to your needs. Contact us for more information.
-
Product Health, Safety and Environment Services
Our experienced HSE experts offer various health, safety and environment services: Safety data sheet (SDS) support (SDS classification, labelling) in most EU languages, including online access and QR links; Controlled substances, precursors, highly active substances and other restricted chemicals (in-clud...
-
Product Excipients
We offer a broad portfolio of excipients, covering all dosage forms including tablet, capsule, syrup, oral dispersible tablet, sachet, gel and suppository.
Our team of experts with commercial, technical and scientific backgrounds is at your service at locations in 18 countries. With our...
-
Product Supply Chain Services
With a dedicated team of experienced supply chain specialists, we go far beyond conventional offerings to provide you with innovative and efficient supply chain solutions. With three strategically placed warehouses in Switzerland and Germany, we are able to store and distribute your products in a ...
-
Product Simaline™ Wo
SIMALINE™ WO is an excellent water-in-oil emulsifier and effectively stabilizes all types of oils at low concentrations with textures ranging from lotions to thick creams.
• SIMALINE™ WO is compatible with a wide range of oils • It can be used to formulate water-rich W/O emulsions, with ...
-
Product Simulsol™ Pha
SIMULSOL™ PHA products are hydrophilic non-ionic surfactants used as solubilizing or emulsifying agents in oral or topical formulations.
This surfactant range includes: ethoxylated fatty acids, castor oils and fatty alcohols
All the products in the SIMULSOL™ PHA range comply with the ...
-
Product Amonyl™
The AMONYL™ product range is composed of betaine derivatives used for their foaming and cleansing properties.AMONYL™ products are amphoteric surfactants and can therefore be combined with other cationic, anionic or non-ionic agents under certain conditions.https://www.seppic.com/en/amonyl-range
...
-
Product Montane™
MONTANE™ range is comprised of different sorbitan ester grades that can be used to formulate water-in-oil emulsions for oral, topical and injectable formulations.
• MONTANE™20 PHA PREMIUM: Sorbitan laurate • MONTANE™60 PHA PREMIUM: Sorbitan stearate • MONTANE™80 PHA PREMIUM: Sorbitan oleate ...
-
Product UNI-PURE® GA P100
Modified Corn Starch
Gelatin replacement for Veggie Softgels
USP/NF, Ph. Eur.

-
Product Aqualon™ ethylcellulose
Aqualon™ ethylcellulose (EC) is a cellulose ether distinguished by its versatility. Aqualon™ EC is soluble in a wide range of organic solvents and is typically used as a non-swellable, insoluble component in matrix or coating systems. Aqualon™ EC can be used to coat one or more active ingredients of a...
-
Product Aqualon™ CMC BET sodium carboxymethylcellulose
aqualon™ CMC BET sodium carboxymethylcellulose are viscosity modifiers for diluents and excellent suspending agents, easily dispersible in water, and compatible with most active ingredients. To learn more visit https://www.ashland.com/industries/pharmaceutical/parenteral-dosage/aqualon-cmc-ph-bet
-
Product Aquarius™ film coating systems
aquarius™ line of fully formulated coating solutions are practical, efficient, and elegant and they provide effective, high-quality coatings that offer an optimum balance of film strength and adhesion, even for challenging cores and release profiles. The line includes titanium dioxide free option...
-
Product Benecel™ hypromellose
Benecel™ products are high purity, water-souble, nonionic cellulose ethers. Benecel™ hypromellose (hydroxypropyl-methylcellulose or HPMC) is a versatile excipient with a variety of applications. HPMC is the most widely used polymer in hydrophilic matrix systems with widespread use in controlled...
-
Product Blanose™ sodium carboxymethylcellulose
Blanose™ CMC are anionic, water-soluble cellulose ethers, produced by reacting alkalicellulose with monochloroacetic acid under controlled conditions. Blanose™ CMC is available in a variety of grades with different degrees of substitution,viscosity and particle size to meet specific formulation requirement...
-
Product Cavamax* native cyclodextrins
The molecular structure of cyclodextrins creates a bucket-like cavity that can complex with molecules or functional groups on molecules to improve solubility of poorly soluble compounds. The same mechanism makes these excipients capable of masking unpleasant taste/odor and stabilizing drugs that are prone ...
-
Product Cavitron™ cyclodextrins (hydroxypropyl betacyclodextrin)
cavitron™ cyclodextrins (hydroxypropyl betacyclodextrin) are the perfect substances for increasing solubility and enhancing bioavailability. They are manufactured to high purity standards for low bioburden and endotoxin.
To learn more visit https://www.ashland.com/industries/pharmaceutical/oral-...
-
Product Ferronyl™ iron supplement
Ferronyl™ iron supplement isan ideal source of essentially pure iron with low toxicity,minimal metallic taste andexcellent bioavailability. Ferronyl™ iron supplement is elemental iron (Fe) with high (> 98%) iron content,manufactured by the chemical decomposition of iron pentacarbonyl. The resulting iron...
-
Product Klucel™ hydroxypropylcellulose
Klucel™ hydroxypropylcellulose (HPC) is a nonionic water-soluble cellulose ether with a remarkable combination of properties. It combines organic solvent solubility, thermoplasticity and surface activity with the aqueous thickening and stabilizing properties characteristic of other water-soluble cellulose ...
-
Product Natrosol™ hydroxyethylcellulose
Natrosol™ 250 hydroxyethylcellulose (HEC) is a nonionic, water-soluble cellulose ether. Natrosol™ 250 HEC is easily dispersed in cold or hot water to give solutions of varying viscosities and desired properties, though it is insoluble in organic solvents. It is used in solutions and gels to control rheolog...
-
Product Pharmasolve™ N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone
Pharmasolve™ N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) is a versatile solubilizer for one-component systems. It is a water-miscible polar aprotic solvent with high interfacial activity. Pharmasolve™ NMP is manufactured in a facility with ISO 9001:2015 and EXCiPACT GMP certifications. It is used as a drug solubilizer an...
-
Product Plasdone™ povidone
Plasdone™ povidones are a family of water-soluble polymers based on N-vinylpyrrolidone that combine a unique set of properties for application in a wide variety of dosage forms. Plasdone™ povidones are commonly used as binders for the development of tablet formulations, whether manufactured by wet granulat...
-
Product Plasdone™ S-630 copovidone
Plasdone™ S-630 copovidone is a 60:40 random, linear copolymer produced by the free radical polymerization of N-vinyl-2-pyrollidone and vinyl acetate. The pyrrolidone ring is responsible for excellent water solubility, adhesion, film forming and solubilization properties, while the vinyl acetate monom...
-
Product Polyplasdone™ crospovidone
Polyplasdone™ crospovidone superdisintegrants are synthetic, insoluble, but rapidly swellable, crosslinked homopolymers of N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone. Crospovidone provides rapid disintegration and dissolution to oral solid dosage forms. Polyplasdone crospovidone particles are granular and porous compared ...
-
Product viatel™ bioresorbable polymers
viatel™ bioresorbable polymers control release over time. These polymers are the building blocks for developing long-acting injectable depots, an established technology to improve therapeutic efficacy and improve patient compliance. Viatel polymers are typically formulated into microspheres, solid impl...
-
Product Benecel™ XRF HPMC
Benecel™ hypromellose (hydroxypropyl-methylcellulose or HPMC) is a versatile excipient with a variety of applications. HPMC is the most widely used polymer in hydrophilic matrix systems with widespread use in controlled-release dosage forms.
benecel™ XRF HPMC is the latest addition to the Benecel™ famil...
-
Product vialose™ trehalose dihydrate
vialose™ trehalose dihydrate is a premier performance sugar that is resistant to acid hydrolysis and enzymatic cleavage. It is used to protect and shield biologic APIs, recombinant proteins, and monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) from degradation and aggregation and to stabilize and protect valuable componen...
-
Product Klucel™ xtend hydroxypropylcellulose
Klucel™ Xtend HPC extended release matrix former is the new product in the Klucel™ line, offering unsurpassed process versatility and release profile efficiency. This step change product has been shown to match the release profile of widely used hypromellose controlled-release formulations with half the po...
-
Product Klucel™ xtend hydroxypropylcellulose
Klucel™ Xtend HPC extended release matrix former is the new product in the Klucel™ line, offering unsurpassed process versatility and release profile efficiency. This step change product has been shown to match the release profile of widely used hypromellose controlled-release formulations with half the po...
-
Product Polyplasdone™ plus multifunctional disintegrant
Polyplasdone™ Plus multifunctional disintegrant is a direct compression superdisintegrant containing silica and lubricant. This highly effective new product provides enhanced flow properties, self-lubrication, and enhanced tablet performance, improving overall manufacturing through-put time. Polyplasdone™ ...
-
Product Povidon Iodine Solution
Unilab chemicals and pharmaceuticals pvt. Ltd offers a wide range of products which includes povidon iodine soln. Application: povidon iodine soln. 5% w/v for topical use. Active ingredient: povidon iodine ip/usp 5% w/v. Contact us for more information.
Excipients
From coating and binding agents to ointment bases, antioxidants and more, search a wide range of excipients from hundreds of international suppliers online at CPhI Online.
The word excipient, derived from the Latin phrase excipere - to receive, to except, or take out, refers to any component other than the active pharmaceutical ingredient contained in solid dosage forms or used to manufacture a finished pharmaceutical product (FPP). Excipients play a significant role in the formulation and administration of dosage forms and the drug development process. They affect the aesthetics, processing capability, bioavailability, and performance of the drug substance and the compliance of patients using a specific dosage form.
Excipients can either act as carriers (basis or vehicles) or diluents, etc., of the active ingredients or components. They aid in the drug product manufacturing process and also enhance the bioavailability, stability, appearance, storage integrity, effectiveness, safety, and delivery of the drug product during use.
Excipients and active ingredients form the major components of drugs. However, excipients make up the bulk of drugs and medicines, making about 90% of each drug’s composition. These substances are mostly pharmacologically inactive or inert and serve specific purposes. However, as opposed to popular assumptions, excipients are not always inactive or inert and may result in side effects or adverse reactions if misused.
The wrong choice, quality, combination, or amounts of excipients used can have devastating effects on the patient’s health. Like every other drug component, these inactive ingredients need to be standardized, regulated, and validated to ensure the safety of the chemical decomposition products for consumption.
Pharmaceutical products contain not just active ingredients but also other components that largely influence the drug’s pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics.
There are a variety of excipients contained in FPP dosage form. The type of excipient included in each FPP is determined by the active ingredient contained, route of administration, and intended dosage form. For example, a tablet formulation is an oral dosage form and usually contains binders, fillers, diluents, disintegrators, and lubricants.
How many excipients are used in the pharmaceutical industry?
In almost every drug form, there is an excipient or combination of excipients and there are over 1,000 excipients used to manufacture finished pharmaceutical products.
Initially, excipients consisted of biologically inert, structurally simple, and naturally derived substances such as minerals, wheat, sugar, etc. Nevertheless, in recent times, the production of novel drug formation systems has led to several new and novel excipients such as coprocessed excipients.
How are pharmaceutical excipients classified?
Excipients are classified based on their route of administration (oral, parenteral, and topical excipients, etc.), on origin (Organic and inorganic chemicals), and by functionality (Fillers, emulsifying agents, excipients for direct compression, etc.). These classifications have subdivisions.
The oral dosage forms make up most dosage forms administered to patients due to their formulation, ease of formulation, administration, and transport, among many others. Given this, the main excipients are found in solid dosage formulations and serve as high revenue drivers in the pharmaceutical excipient market. Some main excipients include calcium phosphate, dicalcium phosphate, starch, magnesium stearate, gelatin, and several others.
Role of excipients in drug formation
The traditional use of excipients has been modified by the development of novel drug delivery systems. Beyond increasing the bulk of formulation and simplifying the manufacturing process, excipients perform a variety of roles such as binding ingredients, boosting patient’s acceptance and compliance (by masking unpleasant odors or tastes), enhancing the stability of active ingredients, extending viability and acting as diluents (for example, microcrystalline cellulose, starch), etc.
How do excipients affect the performance of drug products?
The bioavailability of drugs refers to the amount of and rate at which a drug’s active ingredient is being made available at its active site. Although excipients are generally pharmacologically inert or inactive, they can interact with drugs in various dosage forms and influence physiologic factors during absorption, distribution, and elimination.
Excipients that affect the bioavailability of drug formulations are capable of influencing their overall performance, either in a positive way by improving performance and therapeutic effect, or in a negative way by diminishing them. The extent of the impact is dependent on the dose and potency of the formulation, site of absorption, therapeutic window, or rate-limiting factors of drug absorption, and many other factors.
Excipients can result in pharmacokinetic interactions through modulation of intercellular tight junctions, metabolic enzymes, and transporter proteins. The bioavailability of drugs can be affected by excipients’ solubility at absorption sites, liability to enzymatic interaction and degradation, drug-excipient interactions, etc.
Poorly water-soluble drug formulations will result in low and erratic bioavailability. However, lipid-based, surfactant-based, and polymeric excipients have high solubility rates and can improve bioavailability.
Ionizable and soluble excipients can exhibit charge interactions with APIs. For example, positively charged drugs such as polymycin and neomycin can form precipitations in the presence of sodium alginate.
Excipients can also affect the dissolution kinetics of drugs by altering the medium in which the drug dissolves or reacting with the drug. Suspending agents help increase the viscosity of the drug vehicle, which, in turn, reduces the dissolution rate from suspensions. For example, an excessive amount of magnesium stearate in tablet formulations can repel water, and limit the rate of drug dissolution, thereby decreasing the rate of drug absorption and the bioavailability of the drug. Formulation processes such as wet granulation, also have a huge effect on the bioavailability of drugs.
Best practices in dealing with novel excipients
Novel excipients are simply excipients used in drug formulations or through a route of administration for the first time. These excipients could be new chemical products or a previously used and certified excipient that hasn’t been established for use by humans or through a specific administration route.
For example, new solubilizers are required to solve the drug delivery challenges associated with poorly water-soluble drugs. New and novel excipients usually include natural polymer excipients, synthetic polymers, natural polymers modified with/by synthetic polymers, coprocessed excipients, and synthetic polymers modified by other combinations or smaller molecules. Some examples of novel excipients include albumin, Soluplus, Kollicoat Smartseal 3D, etc.
Novel excipients play an essential role in producing and introducing new, advanced, and safer drugs to the pharmaceutical market. However, due to global regulatory policies, there have been various challenges to the development of new excipients. Regardless of this, more companies are adopting innovative excipients to develop novel drug formulations. This has given way for more recent and advanced drug delivery systems to provide safer and more effective drugs for patients and more convenient administration routes. The concept of novel excipients has further broadened the scope of pharmaceutical science.
What drug development challenges do drug sponsors encounter during the manufacturing process that could be addressed by using novel excipients?
With new and significant innovations in the pharmaceutical industry, such as the development of novel drugs for the treatment of rare and orphan diseases, the need for new and advanced excipients to boost drug delivery systems is on the rise. As drug products evolve and increase in structural complexity, the formulation challenges also increase. The use of novel excipients significantly impacts the drug development process, creating various treatment types available to patients, and introducing new therapies into the pharma market.
The development and evaluation of NCEs are costly to process compared to the process of modification of previously established excipients. This issue can be addressed by the development of multi-functional novel excipients, which can perform several roles such as boosting drug stability and bioavailability, controlling API release based on therapeutic needs, etc. These excipients’ production results in a significant decrease in manufacturing cost, hastens the drug development process and improves drug sales and company growth.
Other challenges encountered by sponsors include the need for solubility, stability and permeability modulation, loss of compaction due to wet granulations and high-moisture compatibility of drugs, and increased demands for ideal filler-binders for direct compression, among others.
What are the latest guidelines for novel excipients?
Currently, novel excipients are not evaluated and regulated independently. However, they can be submitted, evaluated, and regulated as part of an IND or IMPD. There are no clear-cut or approved regulatory pathways provided by the FDA or the European Medicines Agency (EMA) to independently assess the efficacy and safety of novel excipients. This present a major barrier and set-back to the pharmaceutical excipient industry and global market, limiting innovation of new and novel excipients regardless of whether they are modifications of existing chemical entities or new chemical entities (NCE).
Although the International Pharmaceutical Excipients Council has been advocating since 2011 for the implementation of a novel excipient approval process by the FDA, the evaluation process hasn’t been put in place. Implementing a novel excipient review or evaluation program will significantly drive the pharmaceutical industry and give room for innovative drug formulations.
Top trends in pharmaceutical excipients
The pharmaceutical excipient industry is rapidly evolving and is continuously searching for new ways to provide innovative and advanced drug formulations for therapeutic purposes. According to a recent study, the global pharmaceutical excipient market is anticipated to experience massive growth over the 2019-2025 forecast period. The market size is expected to reach an estimated value of USD 9.7 billion, at a steady CAGR of 5.8%.
The pharmaceutical excipient markets’ top trends include the increased use of nanotechnology, patent expiries, increased demand for multi-functional excipients, a competitive market landscape, the binders segment taking the lead as the fastest-growing market, and North America possessing the largest share in the global market. The pace of the global pharmaceutical excipient market growth serves as a pharma trend barometer.
Who are the top players in the pharmaceutical excipients industry?
Due to the increasing need for pharmaceutical excipients and the exponential growth of the global pharmaceutical excipient market, there has been a rising competition between excipient manufacturer and excipient supplier in this industry. Amongst the competitor is top players that have largely contributed to the growth of the pharmaceutical excipient industry.
Some of the top players in the pharmaceutical excipient industry include BASF SE, Evonik Industries AG, Lubrizol Corporation, Croda International Plc., Ashland Inc., Avantor Performance Materials Inc., The Dow Chemical Company, Innophos Holdings Inc., Archer Daniels Midland Company, Colorcon Inc., Kerry Group, Merck, Signet, and FMC Corporation amongst many others. The collaborative efforts, expansions, and agreements of these excipient manufacturers to boost the growth of the market.
What is the revenue, sales, and price analysis of top manufacturers of pharmaceutical excipients?
The binder’s segment is anticipated to dominate the pharmaceutical excipient market during the forecast period. In 2017, the pharmaceutical excipients market achieved a total revenue of about USD 4256.3 million, and this revenue is anticipated to grow at a rate of about 6% until 2023. The growing income levels, increasing health expenditures, and improved health awareness globally reflect the many potentials of pharmaceutical excipients.
In addition, the organic segment of the excipient market, including carbohydrates, proteins, petrochemicals, and others, is likely to contribute to the growth of the pharmaceutical excipients market. The rising demand for and application of organic excipients in pharmaceutical industries is expected to drive sales and market growth. Given this, the organic chemicals market share segment is anticipated to grow faster than the inorganic market segment. This benefits the manufacturers and the patients alike.
It is expected that top pharmaceutical excipients manufacturers in North America will record a spike in revenue generation during the forecast period. It would be influenced by the development of advanced infrastructures as well as better investment policies. Several pharmaceutical excipient manufacturing companies in this region participate in projects contributing to the growing demand for novel and advanced drugs.
In addition to this, the massive investments being made are also significant contributors to the anticipated revenue generation. Companies in Europe are also expected to partake in the revenue generation. Also, the Asia Pacific region is expected to experience an increase in revenue generation through structural investments.
Prices of manufactured excipients across various regions globally are dependent on the excipient supply and excipient demand chain within each region. Also, this is dependent on the quality of excipients being produced in each of these regions.
What key factors drive the global pharmaceutical excipients market?
The pharmaceutical drug market size is growing rapidly, and its growth is expected to drive positively impact the growth and size of the pharmaceutical excipient market. In addition to this, several other key factors have driven and are still driving the pharmaceutical excipient market’s growth. Some of these factors include advancement in functional excipient development, increased use and expansion of biopharmaceuticals, large patient population base, the prevalence of chronic diseases, the rapid growth of the biosimilar industry, increasing demand for generic drug, patent expiries, and development of multi-functional and co processed excipient. These key factors have primarily contributed to the growth of the pharmaceutical excipient market during the forecast period.
Excipients play a variety of roles in drug formulations and make up the bulk of almost every drug. The pharmaceutical industry is rapidly advancing through biotechnology to provide safer and more effective drugs for therapeutic purposes. Novel excipients are gaining worldwide attention, and the push for a novel excipient review and evaluation system is growing stronger. In a few years from now, there may be the creation of an established novel excipients evaluation process or system. The establishment of these evaluation processes would allow companies to grow, deliver on-demand health needs to patients, and spur the global pharmaceutical excipients market’s growth.
References
https://www.pharmaexcipients.com/pharmaceutical-excipients-some-definition/
https://www.biopharma-excellence.com/news/2019/12/13/best-practices-in-dealing-with-novel-excipients
https://www.pharmaexcipients.com/wp-content/uploads/attachments/CO5_2013_RGB_80-83.pdf?t=1446883266
https://www.slideshare.net/mobile/SalmanBaig6/novel-excipients
https://www.pharmaexcipients.com/news
References
Upcoming Events
-
-
-
CPHI & PMEC India 2024
India Expo Centre, Greater Noida, Delhi NCR
26 Nov 2024 - 28 Nov 2024
Pharmaceutical Industry Webinars
-
Webinar Fragment-Based Oligonucleotide and Oligopeptide Synthesis
-
30th Jul 2023
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
-
Webinar GMP Rationale for Sterile High-Potency/Toxic Pharmaceuticals
-
18th June 2024
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
-
Webinar Unlocking Opportunities in the Growing Pharma Landscape of The Middle East
-
5th June 2024
-
3pm CET / 9am EST
-
-
Webinar Exploring Technological Trends in the Future of Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
-
23rd May 2024
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
-
Webinar Achieving Manufacturing Excellence Through Digital Transformation
-
16th April 2024
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
-
Webinar Made in Africa: What’s Driving Pharma Manufacturing
-
28th March 2024
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
-
Webinar Case Study: Risk Management for Annex 1 Sterile Production EMS
-
28th February 2024
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
-
Webinar Innovative Strategies for B2B Pharma Marketeers: Driving Value through Content
-
20th February 2024
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
-
Webinar Revolutionizing Pharma: Data and AI Unleashed
-
18th January 2024
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
-
Webinar Optimal Temperature: Elevating Biologics Cold Chain Excellence
-
16th January 2024
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
-
Webinar Market Outlook – The Biggest Pharma Trends of 2024
-
12th December 2023
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
-
Webinar The Next Frontier – Emerging Opportunities in the LATAM Pharma Market
-
21st November 2023
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
-
Webinar Vistamaxx™ MED - imagine the possibilities for healthcare product performance
-
10th October, 2023
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
-
Webinar Co-processing: A Multifaceted Approach for Enhancing Density & Powder Flow
-
19th September 2023
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
-
Webinar The Outlook for Cell & Gene Therapy Manufacturing
-
28th June 2023
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
-
Webinar Contract Packaging Outlook: Growth Trends within the Commercial Packaging Sector
-
25th May 2023
-
4pm CET / 10am EST
-
Position your company at the heart of the global Pharma industry with a CPHI Online membership
-
Your products and solutions visible to thousands of visitors within the largest Pharma marketplace
-
Generate high-quality, engaged leads for your business, all year round
-
Promote your business as the industry’s thought-leader by hosting your reports, brochures and videos within your profile
-
Your company’s profile boosted at all participating CPHI events
-
An easy-to-use platform with a detailed dashboard showing your leads and performance






















-comp286402.jpg)






















































































































































.png)












































































































.png)

.png)



.jpg)